Description and characteristics of mountain clematis, planting and care
Clematis (clematis) is the most popular climbing plant for vertical gardening of the territory. Liana in a short period of time is able to wrap around a gazebo, pergola, or arch. In the early 19th century, a plant was discovered, which was given the name mountain clematis. The following is information on the characteristics of the species, popular varieties, as well as planting, care, reproduction of vines.
View characteristic
Mountain Clematis is a liana, the whips of which can reach a height of 8 meters. Pink, white, lilac, cream flowers form on last year's shoots. They can be single, or collected in inflorescences, decorated in the form of scutes and panicles. The trifoliate, pointed leaves are green in summer and yellow in autumn.
Mountain Clematis climbs to a height with the help of petioles, with which it clings to the support. Its flowering begins in late spring.
This plant is frost-resistant, so it can be grown in regions with fairly cold winters.
Popular varieties
The most popular varieties of mountain clematis grown in garden plots are Rose Rubens and Montana Grandiflora.
Rubens pink
The main decoration of this variety is large pink flowers. Rubens Rose is also prized for the subtle vanilla aroma emitted by the plant during flowering. Clematis buds are laid in autumn, bloom in late May or early June.
Montana Grandiflora
The variety builds up powerful whips, capable of covering a gazebo or pergola in a short period. The flowers of clematis are large, looking like four-pointed stars. Flowering lasts throughout June. In addition to the fact that the vine has an aesthetic appearance, a pleasant fragrance emanates from it.

Landing
For the development of mountain clematis, the place in which it will be planted, the composition of the soil, and the timing of planting are of great importance. It is also important to choose the right healthy planting material so that it will not be affected by various diseases in the future.
Site requirements
Mountain clematis is a light-loving plantation. In a shaded area, the growth and flowering of clematis will be weak. But, at the same time, you need to make sure that the root system of the vine is cool. To do this, sprinkle it with mulching material.
Soil selection and preparation
Mountain clematis prefers to grow on loose, fertile soil. Heavy, clayey soil should be lightened by adding sand and compost.According to the degree of acidity, the soil should be neutral or slightly alkaline.

Timing
Mountain clematis is planted in spring or autumn. The container-grown seedling can be planted even in summer. If the gardener did not manage to plant clematis in the fall, he can keep it until spring by placing it in a cool room. To prevent the roots from drying out, they need to be sprinkled with a mixture of sawdust and sand.
The choice of planting material
You need to purchase mountain clematis seedlings from trusted sellers. Vine shoots should be strong, with elastic leaves. There should be no signs of disease on them, otherwise the young plant may die, not even having time to take root. It is best to purchase clematis in closed-root containers.
Landing scheme
A pit for planting clematis is dug out according to the scheme 60 × 60 × 60. A drainage of stones or expanded clay is poured onto its bottom with a layer of about 10 centimeters. If the soil on the site is infertile, compost, dolomite flour, superphosphate are added to the planting pit.
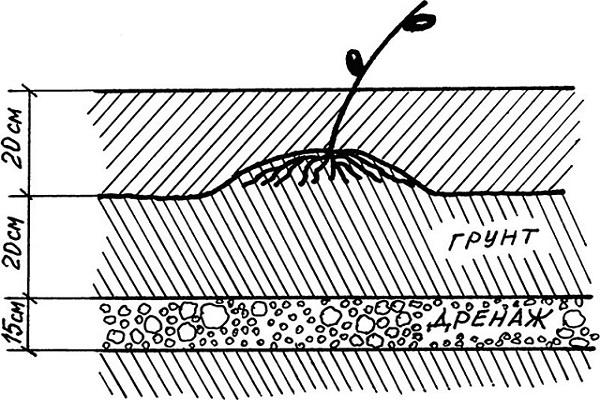
Care
In order for clematis to please for a long time with their flowering, they need to be looked after: watering, feeding, weeding the ground around them, preventing the appearance of diseases and pests.
Watering
Mountain Clematis loves moisture, so it needs frequent watering, at least 1 time per week. Around the vines, you can dig in several pots with small holes, and pour water into them if necessary. Through the holes, the liquid will slowly penetrate to the roots, moisturizing them in dry summers.
Loosening and weeding
Around clematis, you need to constantly remove weeds by hand or by weeding. This procedure is especially required for young clematis: if the weeds are not plucked, it will not allow weak lashes to develop. When weeding, the soil is simultaneously loosened, which promotes the penetration of water and air to the root system.

Top dressing
In the first year, clematis can not be fed, especially if they are planted in fertilized soil. The next year, they are fed first with nitrogen to build up green mass, then, during the budding period, with potassium and phosphorus. The same composition is used to fertilize clematis after flowering.
Trimming group
Mountain clematis belongs to the 1st pruning group. These vines do not need annual pruning, it is enough to remove only damaged branches. For adult plants, rejuvenating pruning is done, removing half of the shoots after flowering. The remaining old branches are removed the next year.
Note! Cutting off shoots when planting is not recommended.
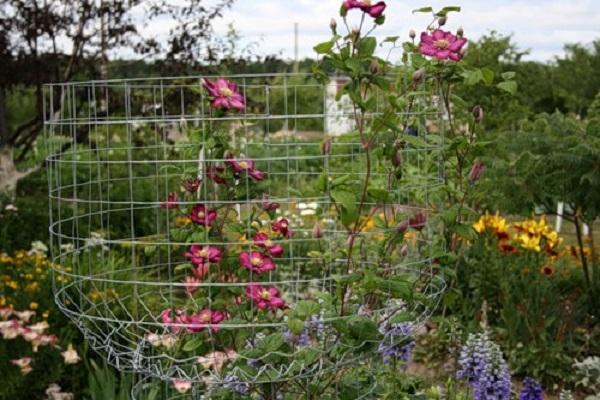
Support
Since the shoots of mountain clematis are able to climb to a great height, you need to install a support around the plant, or plant it near the already dug pillars. Supports do not have to be vertical, they can be in the form of arches, pyramids, fan structures. Also, clematis can be placed between the bushes by pulling several ropes or lines between them.

Diseases and pests
Diseases and pests are easier to prevent. For this, overheating of the soil must not be allowed; it is forbidden to fertilize the vines with fresh manure. In the fall, you need to burn plant residues that contribute to the spread of pathogenic microorganisms.
Fusarium
With fusarium in clematis, the lower parts of the shoots turn black. Fungal disease appears due to high humidity at the roots of the plant.
To prevent fusarium, clematis is sprayed in spring and autumn with a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid.
Wilt
This is the most common fungal disease among clematis. Pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the tissues of the vines through the injured parts. Shoots darken and wither quickly. In the initial stages of the disease, plants are sprayed with fungicides. If the disease has spread to the entire plantation, it is dug up and burned.

Nematodes
These are microscopic parasitic worms that inhabit all parts of the vine.Root nematodes are especially dangerous, as a result of the vital activity of which the cells grow, and nodules - galls - are formed on the roots. Infected plants are destroyed, otherwise they can infect the rest of the plantings.
Reproduction
It is possible to dilute clematis on the site in several ways: by seeds, cuttings, layering, dividing the bush.
Seeds
Seed propagation takes place in early spring. Before planting in open ground, they must undergo stratification (aging for 2.5-3 months at low temperatures). To do this, you can keep the seeds in the refrigerator throughout the winter. The seed is soaked in water for 3 days, then planted in the garden to a depth of 1 centimeter.
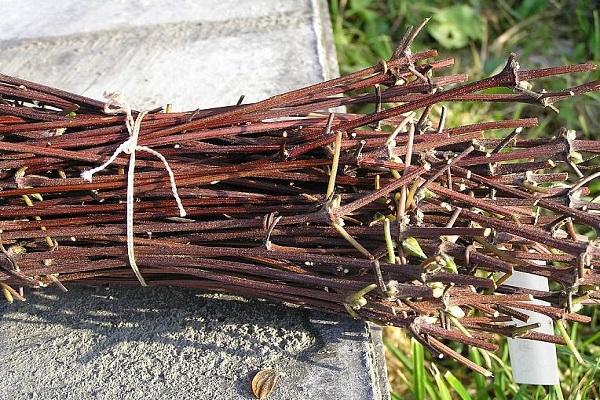
Cuttings
For spring cuttings, well-ripened middle parts of the shoots are used. They are cut, placed in water with the addition of Kornevin for 30 minutes, then planted in a pot. After rooting, young plants are planted in open ground.

Layers
It is best to propagate clematis with cuttings in spring. To do this, the shoots are pinned into small depressions dug out in advance near the clematis. The place of contact of the stems with the soil is watered with water, covered with garden soil. In the fall, rooted seedlings are dug up and transplanted to a permanent place.
By dividing the bush
The procedure is performed with adults over 6 years old, vines. The bushes are dug up, cleared of the ground, carefully divided into parts. Each division should have several shoots and a developed root system.









