Causes and symptoms of African swine fever, danger to humans and how it is transmitted
The owners of cattle farms in Russia are concerned about the safety of animals due to the active spread of African swine fever. Every farmer should study the symptoms of infection, how it spreads, and the potential danger. Also important is the question of whether it is permissible to eat the meat of contaminated livestock.
General characteristics of the disease
Swine plague is a viral infection that is highly resistant to treatment. According to experts, the causative agent of the infection remains viable for 1.5 years. The virus is dangerous for individuals of any age and is transmitted in the natural environment by wild African pigs, rodents, birds, domestic and wild animals that have had contact with infected livestock. People can also contribute to the spread of the disease.
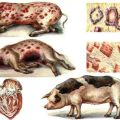
At the initial stage of infection, individuals look healthy, since the main processes take place inside the body. The consequence of infection is multiple hemorrhages in connective tissues, enlargement of the liver, spleen and kidneys. The lymph from swine fever deaths looks like a solid blood clot. Pulmonary edema also occurs.
Reasons for the appearance
The virus was first recorded and studied in 1921 in the eastern part of Africa. In Russia and the post-Soviet states, the virus began to spread since 2008. The intensive spread of infection around the globe is explained by the following reasons:
- migration of people to different countries;
- active build-up of interstate economic ties;
- development of pig breeding and frequent consumption of meat products and lard for food.
The main reason remains the impossibility of complete destruction of the virus in nature. African plague is transmitted by pigs after contact with already infected individuals. The infectious agent also spreads through feed, water, livestock care equipment, and livestock transport.

Disease symptoms
The clinical symptoms of the manifestation of plague have a number of similarities with signs of other diseases. First, pigs' body temperature rises sharply, shortness of breath occurs, thirst increases and appetite is lost. As the infection progresses, the condition of the animals worsens. The African plague can take many forms, depending on the presence of specific signs.
Hyperacute
Lightning current, also called hyperacute, is most common in piglets.Infected pigs show signs such as a fever of 41 degrees, a rapid heart rate, shortness of breath, the formation of bright red spots on the body, and vomiting. With the lightning-fast course of plague, cattle die after 1-2 days.

Acute
An acute course often manifests itself at the onset of an epizootic. The characteristic first symptoms include:
- persistent type of fever;
- body temperature 40-41 degrees;
- rapidly progressive general weakness.
A few days after infection, animals develop anorexia, conjunctivitis, ataxia. Chills, constipation, and vomiting also appear.
Subacute
The duration of the subacute course of the African plague is 2-3 weeks. This stage is manifested by signs of damage to the respiratory organs or the digestive system.
In the case of lung damage, croupous pneumonia develops, due to which the pigs begin to cough violently, the chest hurts and the breathing process becomes more difficult.
The intestinal form is accompanied by enterocolitis, diarrhea, perverted appetite. Animals begin to lose weight, weaken and find it difficult to move. Infected cattle lie a lot and die in most situations. With a favorable outcome, the appetite is gradually restored, the symptoms disappear, and the animals become more active. After recovery, pigs remain carriers of the virus for 10-12 months.

Chronic
The chronic course lasts up to two months or longer. Infected animals have periodic diarrhea, an unstable type of fever, a changeable appetite, and coughing. Pigs begin to lose weight a lot, their skin wrinkles, the ends of the tail and ears die. The exact signs of African plague infection depend on the complications of the secondary infection. Moreover, in each case, the animals gradually become similar to the scum. The death rate varies between 30-60%.
Diagnostic methods
The formation of pronounced cyanotic spots on the body of pigs is perceived as a prerequisite for comprehensive diagnostics in a veterinary clinic. If you notice signs of African plague, you should immediately seek professional help and isolate suspicious individuals from the rest of the livestock. To make an accurate diagnosis, the veterinarian carries out a complex of diagnostic procedures with infected animals.
The specialist makes a conclusion based on the available signs of infection and pathological changes. It is required to find out the cause of the infection and the source from which the virus entered the herd.
It is possible to isolate the virus and its antigen using biological samples and research in laboratory conditions. During the diagnosis, modern technologies are used and an analysis is taken for antibodies, the presence of which is considered as the main factor in identifying an infection.

Treatments for African swine fever
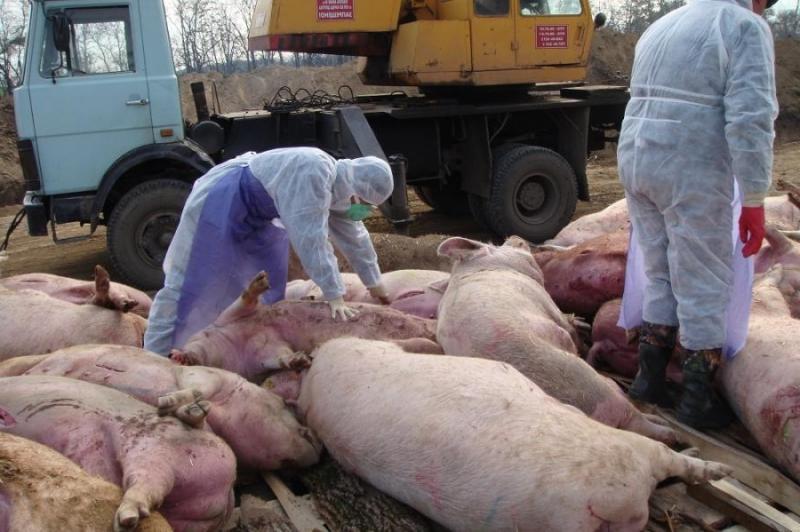
Due to the high degree of infectiousness of plague, sick pigs are destroyed. In addition, scientists are still developing a vaccine against the virus. The main difficulty lies in the fact that the virus often mutates, and the disease is often asymptomatic. In such situations, control measures are ineffective.
How does ASF threaten people?
The African plague virus does not pose a danger to humans, affecting only pigs. Since the plague genome cannot withstand heat treatment of more than 70 degrees, animal meat is allowed to be eaten. Despite this, there is a potential danger in the future if the virus continues to mutate.
As a rule, the infection of livestock affects only the economic component, since high costs are required to eliminate the focus of infection.The spread of the virus leads to the loss of livestock and the need to restore the number of animals.

Prevention measures
Preventive measures that completely eliminate infection have not yet been created. All applied actions are aimed at suppressing outbreaks of infection, combating the active spread of the virus, and reducing the likelihood of infection in healthy individuals. When a plague focus is detected, all animals in the epicenter are destroyed due to the lack of a vaccine. When faced with an infection of the livestock, they take the following actions:
- burning pig carcasses, contaminated feed and livestock care;
- ash is mixed with lime and buried;
- the farm and surrounding areas are treated with a disinfectant solution;
- a quarantine is announced, which ends 6 months after the extreme death of livestock;
- the pig farm is not used for keeping livestock for a year after the end of quarantine.
To reduce the risk of infection of animals, it is necessary to timely vaccinate against classic plague in a veterinary clinic. This will support the immunity of the livestock and increase protection against the virus. Livestock should be kept in a closed area, avoiding free range. With a frequency of 2-3 months, it is required to treat animals and pig farms from blood-sucking parasites. If you notice signs of plague, you should immediately contact the veterinary service.
Also, precautions are taken at the state level. There are a number of regulations that apply to the import of meat products and livestock, including a ban on import from countries where outbreaks have been observed.