Description and characteristics of green currant varieties, cultivation and care
Green currant is a relatively new crop, not as common as black and red. Bred in the 30s of the last century, it only recently began to "conquer" summer cottages and household plots. This is explained by the many advantages and characteristics of this culture.
Features of green-fruited varieties
The main features of the varieties of this culture, in comparison with black and red, are as follows:
- green color of ripe berries, thin skin and sweet taste;
- the berries lack a characteristic sharp "currant aroma";
- high demands on growing conditions;
- late ripening;
- resistance to pests and diseases common with black currant.
Also, the berries of this culture do not cause food allergies, the content of vitamins and microelements in it is higher than in varieties of black and red currants.
Description of the best varieties of green currants
The most popular varieties of green currant are Vertti, Emerald Necklace, Snow Queen.
Vertti
This Finnish variety is characterized by a medium-sized compact bush with a height of 0.9-1.0 meters, light green berries, covered with small brown spots. The taste of the berries is sweet. The crop ripens in late July and early August. The variety is frost-resistant, resistant to damage by powdery mildew, kidney mites.
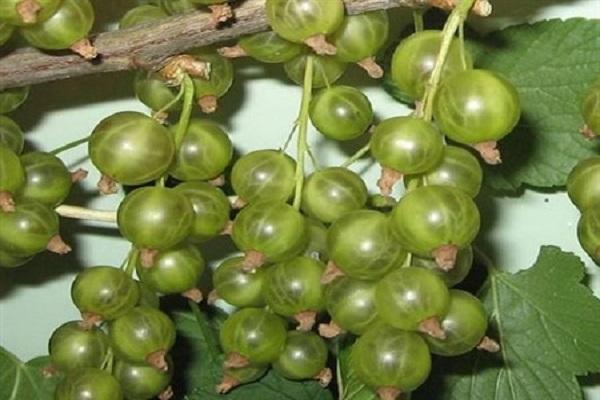

Emerald necklace
Medium late variety of domestic selection. Low-growing (0.5-0.7 meters high) spreading bushes of this variety in mid-August are covered with pale yellow, with an emerald tint, ripe berries that have a sweetish, slightly sour taste. With an average yield, the variety is characterized by high resistance to powdery mildew, medium - to bud mites.
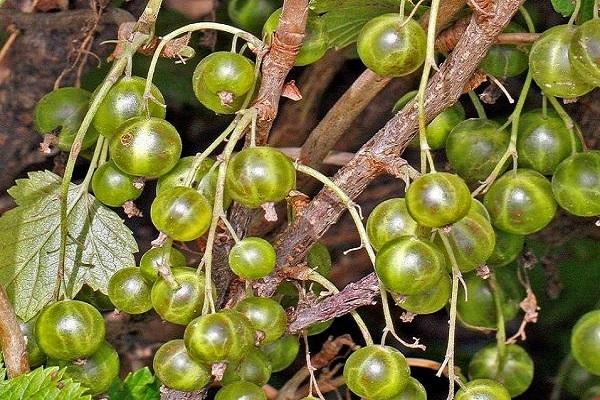
The Snow Queen
A late-ripening variety characterized by a low-growing compact bush, large ripe berries of a light green color. Unpretentious to growing conditions, not damaged by severe frosts, resistant to most diseases and pests of currants. The average yield from 1 bush of green currant of this variety can reach 2.6-3.0 kilograms.

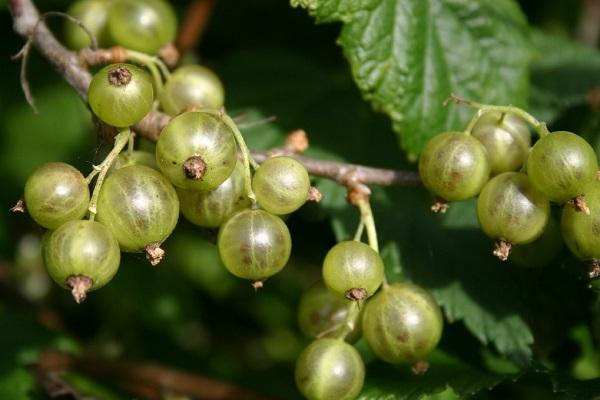
Pros and cons of growing on the site
Like any other crop, green currant has both pros and cons.
The main advantages of this type of currant are:
- Large-fruited - ripe green currant berries weigh up to 4-5 grams.
- Frost resistance - most varieties of this crop can withstand not only winter frosts, but also early spring frosts.
- Hypoallergenic - unlike blackcurrant, green berries do not cause allergies.
- High resistance to diseases, pests - most varieties of modern domestic and foreign selection are resistant to diseases, are weakly susceptible to attacks by pests.
- Invisibility for birds - ripe berries do not stand out against the background of foliage, so that birds do not peck them.
- The sweet taste and thin skin of ripe berries.

The few disadvantages of green currant include:
- late ripening (August-September) - the harvest of green currants ripens much later than varieties of black or red;
- shortage of seedlings - seedlings of this culture are not yet common, therefore, acquiring them is not as easy as the more familiar varieties of black and red currants.
Also, a minor drawback of this culture is the lack of a detailed description of the cultivation technology.
Landing conditions
Planting is the most important stage in growing technology.

Optimal location
The place chosen for planting green currants must meet the following requirements:
- Illumination - the site should be well lit throughout the day.
- The mechanical composition of the soil - the soil on the site should be light, with good moisture permeability.
- Nutrient content - soils with a high humus content (more than 2%), macro- and microelements are suitable for planting and growing green currants.
- Soil water level - Since the root system of the crop is sensitive to flooding, it should be planted in an area with a low water table.
In addition, one should not plant both single bushes and a plantation of green currants in low, wetlands, on drained high peat bogs, near fences, garages.
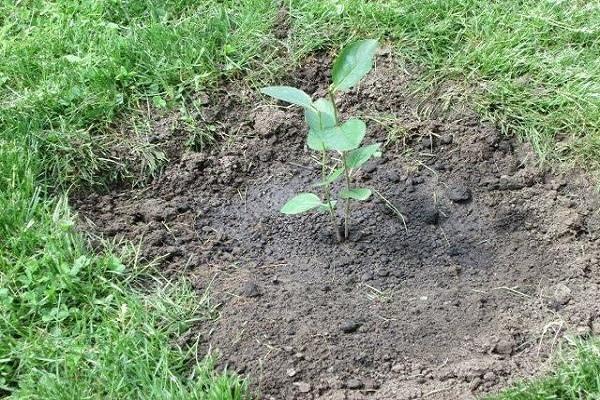

Preparing the soil and planting hole
Preplant tillage includes:
- Destruction of weeds with continuous herbicides (Hurricane, Roundup, Glyphos).
- Surface application of potash and nitrogen fertilizers 10-12 days after the treatment of the site with herbicides.
- Digging (plowing) of the site in the fall to a depth of 25-30 centimeters.
- Early spring loosening of the soil to a depth of 10-12 centimeters.
After the site is prepared, they start digging planting holes with a diameter of 50 centimeters and a depth of 40 centimeters. With a single-row planting scheme, the distance between the centers of the holes should be from 70-80 centimeters (for compact low-growing varieties) to 100 centimeters (for vigorous spreading varieties). When planting a plantation consisting of 2 or more rows, the aisles are made 1.0-1.5 meters in size.
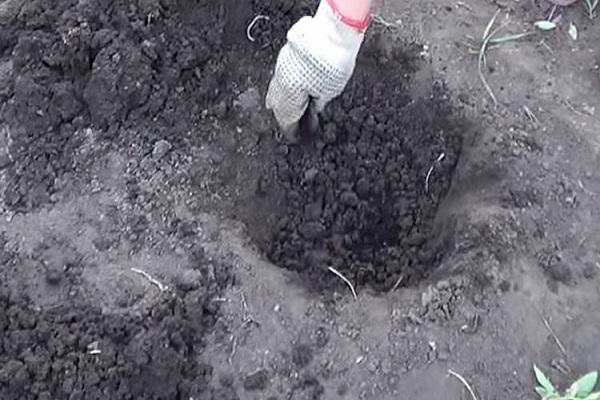

Dates and technology of disembarkation
There are two planting dates:
- early spring - mid-April, after melting melt water and soil warming;
- autumn - early September, after harvesting on a fruiting plantation.
For planting, both in early spring and in autumn, two-year-old seedlings with a well-developed root system, 3-4 shoots should be used.
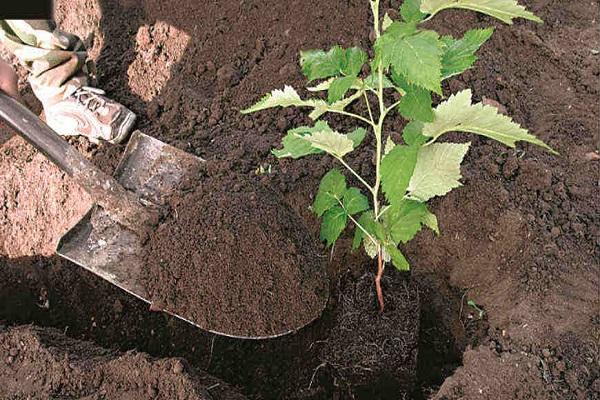
The technology of planting seedlings provides for the following manipulations:
- To fill the hole, a nutrient mixture is prepared, consisting of 2 buckets of humus, 200 grams of simple superphosphate, 30 grams of potassium sulfate, 2 glasses of wood ash.
- Pour half of the nutrient mixture in a mound onto the bottom of the hole.
- The seedling is placed in a prepared planting hole, at an angle of 30-40 , deepening its root collar 8-10 centimeters below soil level.
- The remaining nutrient mixture and fertile soil are poured into the hole, carefully tamped.
- The soil surface near the seedling is covered with a 5-centimeter layer of mulch - dry sawdust, low-lying peat, humus, compost.
A day after planting, the seedlings are watered abundantly. The mulch layer is renewed when it settles.

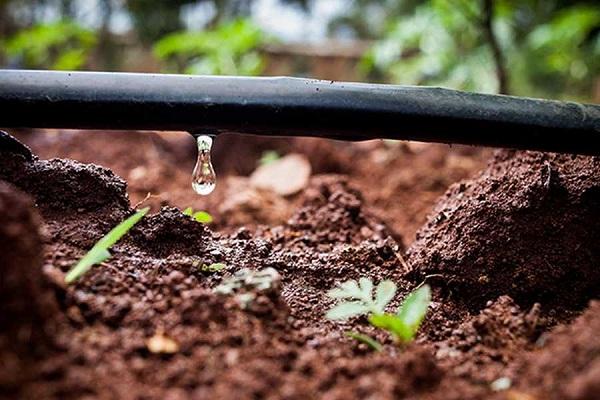
How to properly care for your culture
Plantation care activities include watering, feeding, pruning, pesticide treatments, and shelter for the winter.
Watering frequency
During the growing season, the culture is watered during the following critical periods:
- after landing (April);
- during the flowering period (early-mid July);
- fruiting (August-September).
For irrigation, use settled tap or rain water. Watering rate for 1 bush is 10-12 liters. When watering, water is poured under the root from a bucket or using a garden watering can equipped with a spray nozzle.

We fertilize the bushes
In the first 2-3 years after planting, green currants are fertilized only in early spring, adding 30 grams of ammonium nitrate under each bush.
In subsequent years, two more are added to the early spring feeding:
- during the beginning of fruiting (July-August), in the form of 40 grams of ammonium nitrate, 40 grams of simple superphosphate, 30 grams of potassium sulfate;
- in the fall (after the foliage has fallen), in the form of 50 grams of superphosphate, 35 grams of potassium sulfate.
In addition, once every 3 years, in the fall, 10 kilograms of rotted manure or compost is applied under each bush.

Shaping and trimming
Depending on the season and purpose, the following types of green currant pruning are distinguished:
- Early spring - produced before the start of sap flow, in early to mid-March. In the process of such pruning, dried, frost-damaged and broken shoots are completely removed from the bush.
- Sanitary - performed upon detection of foci of lesions by a kidney mite, sawfly, powdery mildew. With sanitary pruning, all shoots damaged by diseases and pests are removed. The cut shoots are burned.
- Autumn - performed before the plantation leaves for the winter. During this pruning, all weak, unripe, thickening shoots are removed.
- Anti-aging - perform this type of pruning on low-yielding old bushes. When such pruning is performed in early spring, the entire aerial part is cut off, leaving 2-3 cm stumps.
- Formative - performed after planting a seedling. Its essence is to shorten the shoots of the seedling at the level of 3-4 buds from the soil surface.
A sharp tool is used for trimming - a pruner, a garden knife. Slices with a thickness of more than 2 centimeters are covered with garden var.
Preventive treatments
Despite the high resistance of the crop to diseases and pests, it is necessary to carry out preventive treatments against pathogenic microorganisms and insects. For diseases, the plantation of green currant is sprayed with drugs such as Topaz, Tiovit Jet, Alirin-B, Bayleton.
To combat pests, they are sprayed with the following insecticides: Prophylactin, Aliot, Fitoverm, Kleschevit, Lepidotsid, Biotlin.
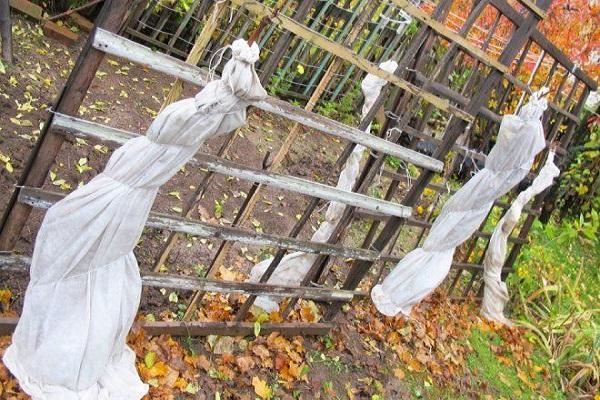
We cover the bushes for the winter
To prevent frost damage to the shoots of the green currant bush, it must be covered for the winter. This procedure consists of the following operations:
- The bush is examined, all unripe annual, old and damaged shoots are cut out.
- Raking up the fallen leaves.
- The remaining shoots are bent to the ground and fixed with metal pegs and bricks.
- The bush prepared in this way, after the onset of stable night frosts, is first covered with straw or sawdust, and then with spruce legs.
If the snow cover during the winter is large, such insulation allows you to completely avoid damage to the shoots, even the most severe frosts.

How to propagate a green culture
The main breeding methods for green currants are as follows:
- Cuttings - for autumn sanitary pruning, cuttings 15-20 centimeters long, with 2-3 buds, are cut from cut shoots. In this case, the cut under the lower kidney is made straight, and above the upper one - at an angle of 45 ... Such cuttings are planted on a pre-prepared bed (school), placing each of them at an angle of 40-45 ... Before rooting, the cuttings are watered moderately. For the winter, rooted bushes are dug up and placed in storage in a cellar or insulated with a layer of foliage, straw, spruce branches.
- Horizontal layering - with this method of reproduction, 2-3 strong shoots are bent to the ground in early spring, fixed with small pins and covered with earth, leaving 5-10 centimeters of the top. In process of rooting and emergence of shoots, the layers are additionally hilled. In autumn, the rooted layers are separated from the mother bush and transplanted to a permanent place.
- Dividing a bush is the easiest way of vegetative propagation. It provides for the division of the old uterine bush with a sharp knife into two parts, followed by transplanting each of them to a permanent place.
Seed propagation (generative) is not used in the conditions of summer cottages and backyards.









