Scheme and schedule of cattle vaccination from birth, what vaccinations are given to animals
Infectious diseases cause significant harm to livestock: death and slaughter of sick animals, reduced productivity, costs of treating sick animals. Vaccination of cattle livestock is the main method of disease prevention. You also need to remember that animals that have had some types of infections become lifelong carriers of the virus.
Importance of the event
To grow healthy livestock, a certain set of measures must be observed: ensuring adequate feeding and keeping conditions, preventing the emergence and spread of diseases. It is vaccination that minimizes the risk of animal disease.
The farms use a preventive vaccine against common diseases. FMD, leptospirosis, anthrax, necrobacteriosis are dangerous for livestock, therefore, vaccinations are given to animals in all regions.
Key recommendations
The effectiveness of vaccination depends on the correct preparation of the vaccination schedule. It is also necessary to consider which vaccine is used:
- inactivated - killed bacteria or their fragments constitute the basis of the substance;
- live - the drug is created from weakened microorganisms - pathogens;
- associated - complex.
The vaccination campaign is carried out at regular intervals. Typically, the vaccine administration schedule is calculated according to the age of the animal. Most of the drugs involve revaccination to consolidate the result.
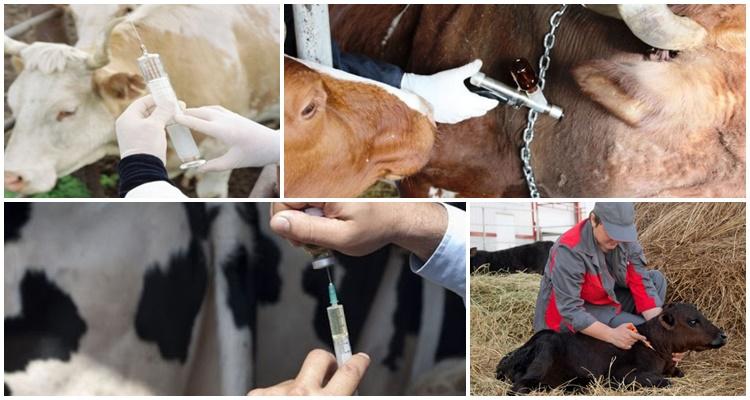

Both large livestock farms and small ones should follow the vaccination schedule. There are no universal vaccination schemes, since factors must be taken into account: the state of health of animals, the conditions of their keeping, the epizootic situation of the region. It should be borne in mind that vaccination of cattle does not cancel the regular check of animal health, since when alarming symptoms appear, sick individuals are separated from the herd in order to prevent the spread of infection.
What vaccinations are used
The list of vaccines recommended for disease prevention will vary by region. It is advisable to use complex vaccines that provide immunity to several infections at once:
- "KOMBOVAK" is used to prevent infection with viral diarrhea, pasteurellosis, infectious rhinotracheitis, parinfluenza-3;
- DEFENSOR 3 - inactivated rabies vaccine;
- "TAURUS" helps the animal's body acquire immunity against leptospirosis, infectious rhinotracheitis, viral diarrhea, parinfluenza-3;
- an associated anthrax vaccine;
- inactivated FMD vaccine.
Vaccination preparations are produced by various companies. Before using substances, it is recommended to verify their effectiveness, safety for animal health.
Calf vaccination
In order for the calf to develop some immunity by 2 months of age, the vaccination schedule must be followed from birth.
Age 12-18 days
Animals of this age are vaccinated against pasteurellosis, parainfluenza-3, infectious rhinotracheitis, and respiratory syncytial infection. Multiple livestock vaccines are recommended. Bovilis Bovipast is available as an injection for subcutaneous administration. The suspension has a light pink tint.
It is used to develop immunity against respiratory syncytial infection, pasteurellosis, parainfluenza-3.
To protect young animals from infectious rhinotracheitis, Bovilis RSP is used. The vaccine can be administered intramuscularly, but intranasal administration is recommended for calves (one milliliter in each nostril).
In regions where the risk of salmonellosis is high, calves 10-12 days old are also vaccinated (1 ml of the drug). After 20 days, the vaccination is repeated, but a dose of 2 ml is administered.
Age 40-45 days
Youngsters at the age of 30 days are initially injected subcutaneously in the neck area with the "Kombovac" vaccine in a volume of 1 ml. The drug is used to prevent roth and coronavirus diseases, from infectious rhinotracheitis, viral diarrhea, parainfluenza-3. The calves are vaccinated again after 15 days. Thanks to Kombovak, the animal's body develops immunity to diseases in two weeks, which lasts for 8 months.
Also, animals at this age undergo revaccination with Bovilis Bovipast RSP. During the life of a calf from one and a half months to four, it is recommended to vaccinate calves against ringworm, anthrax. Subsequently, vaccination against anthrax is carried out annually.
Age 120-130 days
Animals of this age must be vaccinated against infectious rhinotracheitis. Calves 125 days old are given revaccination of the drug against leptospirosis (dose - 6 ml). The first time a vaccination against leptospirosis is given to young animals aged 110 days (the volume of the drug is 4 ml).
Individuals at the age of 135 days are injected with a vaccine (dose of 1 ml) against emphysematous carbuncle. The disease is not considered infectious, but it does kill animals. At risk are calves from 3 months to 3 years old.
Vaccination of adults
Only healthy farm animals are allowed to be vaccinated. Individuals weakened or infected with other diseases are vaccinated after recovery. Vaccination activities are carried out according to the schemes.
For leptospirosis, cows aged 2 years are injected with 8 ml of vaccine. Older animals are given a 10 ml injection.
For vaccination against brucellosis, a live dry vaccine is used. The agent is administered in a volume of 2 ml, subcutaneously. Animals 4-6 months old receive the vaccine for the first time, and again after 10 months. Within 3 weeks after the injection, the body develops immunity, which lasts 11-12 months.
Foot and mouth disease is one of the most common diseases. The disease is acute in young animals. Since there are several subspecies of diseases, vaccines of types A, O, C, "Asia-1" are used. The first vaccination is given to individuals at the age of 6 months. Revaccination is done after 60 days.
Can pregnant cows be vaccinated?
Cows also need regular vaccinations during pregnancy.When drawing up a vaccination, the type of drug is taken into account, how many days are left before calving:
- inactivated vaccine against infectious rhinotracheitis is administered to pregnant cows in the last three months of pregnancy. The drug with a volume of 10 ml is injected intramuscularly twice with an interval of 1 month;
- a month and a half before calving, cows are vaccinated against leptospirosis. The volume of the vaccine is selected depending on the age of the animal;
- pregnant cows are vaccinated against colibacillosis. Primary immunization is performed two months before calving. Re-injection is done after 10 days.
Veterinarians recommend to vaccinate pregnant cows no later than 1.5-2 months before calving. Do not vaccinate against anthrax (period - 30 days after delivery).
Vaccination is a mandatory procedure for raising cattle. Regular examination of animals, a properly drawn up vaccination plan will help preserve animals and ensure the productivity of livestock farming. During the vaccination period, the animals must be carefully cared for.