Analysis of symptoms and treatment of abomasum displacement in cows, diet table
One of the diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in cows is the displacement of the abomasum, characterized by a change in the anatomical position to the right, more often to the left, filled with gases and liquid. During pregnancy, the uterus displaces the abomasum. After calving, he must stand in a normal position, which increases the risk of disease. To diagnose displacement of abomasum in cows, determine the symptoms and further treatment, one should understand the causes of the disease.
What is abomasum in a cow
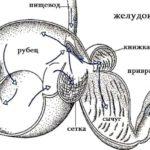
Abomasum, or glandular stomach (lat.abomasus) is a section of the stomach of ruminants, in which digestion occurs under the influence of a digestive enzyme. In adults, the abomasum is located in the lower right part of the abdominal cavity under the right hypochondrium. The thin part of the abomasum connects with the small intestine, and the wide part - with the third section of the stomach (book). The membrane of the glandular stomach is covered with epitheliums that form folds.
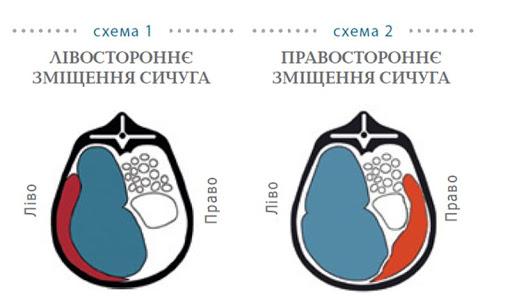
Abomasal displacement (Latin dislocatio abomasi) is a condition of cattle, when the abomasum, expanded by gases, liquid or their combination, changes its anatomical position. Offset is of two types: left-sided and right-sided.
The gases generated inside expand the size of the glandular chamber. In advanced cases, it stretches and takes up a lot of space in the animal's peritoneum. In most cases, the displacement is observed after childbirth, since during pregnancy the uterus increases in size and displaces the glandular stomach. A number of reasons contribute to the development of the disease:
- hypotension of muscle tone of the stomach or intestines;
- stagnation;
- ataxia - violation of muscle movements;
- difficult childbirth and complications after calving;
- insufficient energy in the feed;
- hypocalcemia;
- poor scar filling.
But the main reason for the displacement of abomasum is considered to be an unbalanced diet, improper nutrition, feed capable of rapid fermentation.
Estimated feed intake:
| DM (dry matter),% | Humidity,% | NDK (neutral detergent fiber) in DM,% | Crude fiber in dry matter,% | Starch and sugar in dry matter,% | Crude protein in DM,% | PERSON, MJ / kg DM (nutritional energy of feed) | |
| 1 dry period (60-21 days before delivery) | 30 | 40-55 | 25 | 20 | 15 | 12 | 5,5 |
| 2 dry period (20 days-delivery) | 35 | 40-50 | 25 | 18 | 20 | 14 | 6,5 |
| Newborn period (1-10 days after childbirth) | 40-55 | 30-35 | 30 | 16 | 26 | 16 | 6,9 |
According to the table, you can calculate the ration of the cow in order to avoid diseases of the abomasum. With an excess of dry matter in the feed or overeating, the release of partially digested food into the abomasum increases. The gastric chamber overflows, the movement of the chyme stops, gases are formed. Displacement often occurs due to the presence of fine particles and concentrates in the feed.

Symptoms of the disease
Clinical manifestations with displacement begin in the first four weeks after calving, in 15-20% - immediately after childbirth. The main symptoms are:
- violation or complete lack of appetite;
- dehydration;
- rarely chewing gum;
- milk production decreases;
- bloating of the abdominal cavity, accompanied by colic;
- infrequent bowel movements;
- dark green pasty feces with mucus and a specific odor;
- acetonemia;
- hypotension of the scar.
With a twisted right-sided displacement, the pulse increases to 140 beats / min. Pains due to colic are severe, the animal begins to kick in the stomach and kicks. If the disease is not diagnosed in time and timely treatment is not started, then intoxication of the body develops, and the animal will die.
Diagnostic measures
This disease is common in highly productive cattle in western Europe, Canada and the United States. Disease analysis accounts for 1% to 5% of all cow diseases.
Left-sided displacement is diagnosed in about 85%, and right-sided displacement - about 15% of all cases of displacement.
To make an accurate diagnosis, to determine the dislocation of displacement, three diagnostic methods are used:
- Palpation - first palpate with fingers, and then forcefully press under the right rib. A painful reaction to palpation indicates an enlarged stomach or twisting.
- Percussion - when tapped, the percussion tympanic sound is clear and loud, which indicates fermentation, fullness and accumulation of gases.
- Auscultation - when listening with a stethoscope, crisp sounds appear, which occur due to the bursting of gas bubbles in the tissues.
For reliability, a blood test is taken from a vein to determine the degree of accumulation of ketone bodies and changes in other metabolic processes in the animal's body.
How to treat cattle disease
Treatment is possible in two ways: non-surgical therapy and a surgical route.
Non-surgical treatment includes a number of measures:
- Solutions of salt, glucose and pain relievers are administered intravenously.
- The cow should be hungry for 1-2 days.
- The abomasum is returned to the correct anatomical position.
- Fix the attachment.
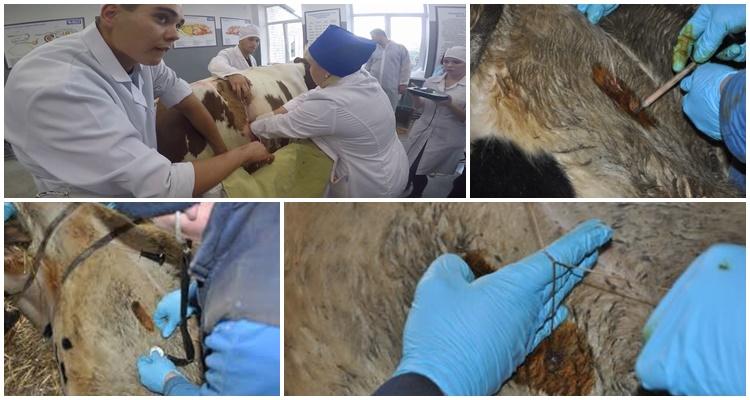
Non-surgical treatment is ineffective, so the main method is surgery, which provides up to 95% of a positive outcome after surgery. During surgery, the walls of the abdominal cavity in the right hypochondrium are dissected, gases are removed, the abomasum is returned to the correct anatomical position and fixed with ligatures.

Possible complications
Changing the anatomical position of the abomasum promotes milk loss and ketosis. Volvulus may occur, resulting in death of the cow.
Problem prevention
The main prevention of the disease is the organization of proper nutrition. The preferred structure of the diet is a fiber content of at least 18% of the DM, concentrated feed - no more than 45%. In order to prevent displacement of the abomasum, it is necessary to prevent and immediately treat the following diseases:
- milk fever;
- myometritis;
- mastitis;
- retention of the placenta, which reduces food intake.
It is believed that cows lying on the left side are less prone to displacement. The displacement of abomasum in pregnant cows, as well as during lactation, in most cases, occurs due to improper nutrition. A balanced diet will prevent gastrointestinal diseases and increase the productivity of the cow.