Causes and symptoms of necrobacteriosis of animals, cattle treatment and prevention
Keeping cattle requires considerable effort on the part of the farmer, especially if the farm has a large livestock. Detection of necrobacteriosis of animals is a disaster for the owner, since milk yields are significantly reduced, efforts and funds are required to treat sick cows, preventive treatment of a healthy herd and barns. Infection of the breeding stock results in significant financial losses.
What is necrobacteriosis
Necrobacteriosis is an infectious disease typical for domestic and wild animals, birds become infected, a person can also be infected. The infection is especially dangerous for cattle and reindeer. The disease is caused by the strict anaerobic bacteria Fusobacterum necrophorum. Bacteria are polymorphic and can be in the form of threads or rods. They form several types of toxins with high pathogenicity. They quickly die under the influence of high temperature (within 1 minute at 100 ° C), oxygen, sunlight. Destroyed by bleach, potassium permanganate, formalin, copper sulfate, and many other chemical compounds.
They remain in the soil for up to 1 month in summer and 2 months in winter. Water or urine infected with necrobacteriosis remains dangerous for 10-15 days. Sources of necrobacteriosis infection are infected individuals that excrete bacteria in urine, feces, putrefactive exudate. The infection is transmitted through infected pastures, drinking places, feeders and drinkers, bedding.
Reasons for the appearance
The main causes of necrobacteriosis outbreaks are errors in keeping animals. The infection can enter the body from grass or soil in pasture, when cows are received from other farms. The "gates" for her are:
- wounds, cuts and abrasions on the legs;
- damage to the genital tract;
- injured hooves not trimmed in time;
- fly and horsefly bites;
- helminthic invasions;
- crowding of livestock in a cold damp barn;
- unbalanced malnutrition;
- long absence of walking.
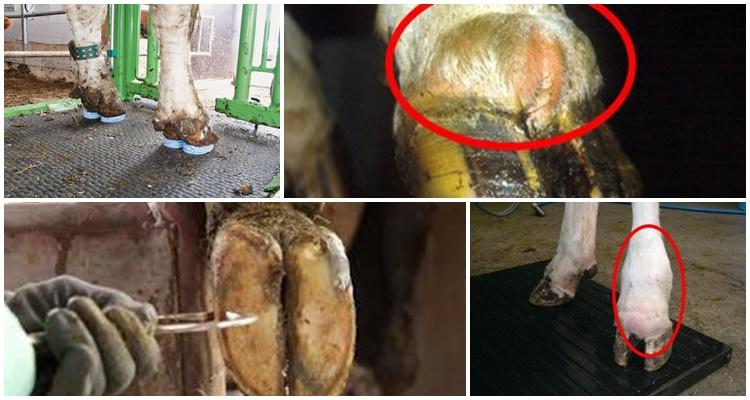
The disease can be acute or chronic, in severe cases, if untreated, malignant lesions occur. Often, necrobacteriosis is complicated by the addition of a secondary infection, for example, bronchopneumonia or an abscess may develop.
Symptoms of pathology
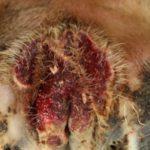
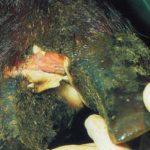
At the initial stage of the disease, a purulent-necrotic lesion usually occurs on a finger or hoof. First, the skin turns red and inflamed. The cow begins to limp, behaves restlessly. One of the animal's hind legs is most often affected. If untreated, the infection rises higher, the legs of the animal, the udder and the mucous membrane of the genitals are covered with ulcers. If a cow licks the affected area, necrobacteriosis affects the lips and mucous membranes of the mouth. The following symptoms are noted:
- Weeping necrobacteriosis sores and wounds cause severe pain, infected cows no longer lean on the injured leg.
- The tissues around the ulcer are dense and edematous, it constantly gets wet.
- In animals, the temperature rises, sometimes above 42 ° C.
- Appetite disappears, chewing gum is lost.
- Body weight and milk yield are reduced.
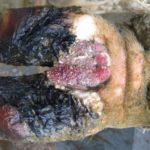
- In advanced cases, ulcers degenerate into a malignant form or gangrene occurs. The animal dies.
If necrobacteriosis of the extremities is not treated in time, not only soft tissue inflammation occurs, joints and bones are affected, pus appears between the muscles, the animal loses the ability to walk.
When the infection spreads to the oral cavity or genitals, it penetrates inside, necrotic foci are formed in the liver, spleen, and abscesses are formed.
Diagnostic measures
To establish an accurate diagnosis, microflora is taken from an ulcer or wound. The smear is examined under a microscope. The bacteria colony is then grown and infected with the isolated material from laboratory mice or rabbits. In the presence of necrobacteriosis, after a while the experimental animals become covered with characteristic ulcers and die. Additionally, the presence of plague, vesicular stomatitis, foot and mouth disease and other diseases is excluded.
Treatment methods
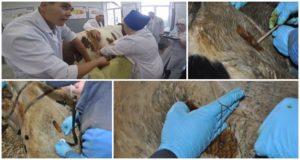
Treatment of necrobacteriosis begins immediately after the detection of the focus of infection. The sick animal is isolated. The wound is cleaned out surgically, necrotic tissue is removed completely, to the borders of healthy ones. Then the tissues are washed with one of the solutions: potassium permanganate, chlorhexidine, furacillin, formalin. Next, the wound is sprinkled with streptocide powder or treated with chloramphenicol or synthomycin.
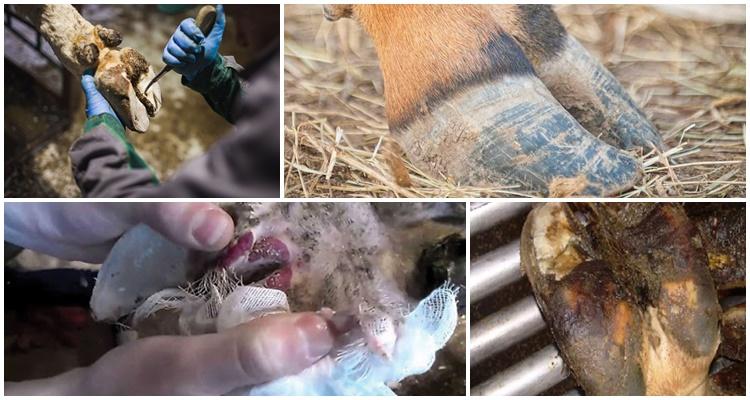
In case of necrobacteriosis of the oral mucosa or genitals, antibiotics are prescribed, for example, tetracycline or chloramphenicol, bicillin and others, with a wide spectrum of action. General baths are organized for healthy animals to prevent necrobacteriosis. The easiest way to make such a container for handling cattle is to dig a trench, the floor and walls of which are filled with concrete and to organize a solid gangway.
The best treatment option: divide such a bath into 2 parts, pour water into one, and a disinfectant solution, for example, a 10% solution of formaldehyde or copper sulfate, into the other. The animals are first driven into a bath with water to wash their hooves, after which they are kept in a bath with an antiseptic for 10-15 minutes. The procedure is repeated 3-4 times with an interval of 5-7 days. The pasture can be used again in 1.5-2 months. If necrobacteriosis is detected on the farm, the barn is cleaned of manure, washed with a disinfectant solution, and the litter is changed.
Restrictive measures are removed from the farm no earlier than 4 months after the recovery of the last animal infected with necrobacteriosis.
General preventive measures
Veterinary medicine has come a long way since the discovery of the disease. Today, so that cows do not get sick with necrobacteriosis, animals are vaccinated. An adult livestock and calves are vaccinated against necrobacteriosis from 3 months of age.
Veterinary specialists examine and treat the hooves of the entire livestock. For prophylactic purposes, they arrange common baths with formalin, copper sulfate or creosote.To prevent cow disease with necrobacteriosis, the barn should be systematically cleaned, manure removed, and the bedding replaced. The room should be warm and dry. It is necessary to protect animals from drafts. The floors are made even so that the animals are not injured.
Animal nutrition should be balanced, including mineral supplements and vitamins. The cows are provided with salt, chalk, bone meal or special vitamin complexes. Walking areas are organized so that the animals do not stagnate.
Since people working on a farm can become infected with necrobacteriosis from animals, first-aid kits are required on farms. After working with sick animals, hands must be disinfected. Sick employees must undergo treatment.
Is it allowed to eat meat and milk from infected cows
If the local treatment is enough for the cow, milk can be consumed after pasteurization.
Important: milk from animals undergoing a course of antibiotic treatment by mouth in large doses must not be sold or processed.
Sick animals, whose treatment is useless, are sent to a sanitary slaughter. The issue of selling meat is decided by a sanitary service doctor who examines the carcass after slaughter. Usually, the carcass area affected by necrobiosis is removed, the rest of the meat is allowed for sale or processing.