Why cows get holes in their sides and fistulas, the meaning of a flipper
A cow walking proudly with a hole in its side is an unusual sight. To animal lovers, such interference with the cow's body may seem unacceptable. However, do not jump to conclusions and rush to protect the animal. The hole made by the surgeon allows you to adjust the cow's nutrition, as well as to provide effective treatment.
What is a hole in the abdominal cavity for?
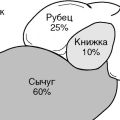
Nature has endowed the cow with a special stomach structure. The body is made up of 4 distinct parts, each of which does its job. Most of the digestive tract of a cow is a scar. The capacity of this "receiver" of chewed food is 200 liters. Numerous microorganisms are responsible for the initial processing of the swallowed feed. Invisible helpers concentrate in the area of the scar and promote the production and synthesis of protein in the pet's body.
The processed food enters the stomach lining. This part of the organ acts as a kind of filter. Small and liquid particles of food are sent to the next chamber of the stomach (book), and large ones in the form of belching return to the animal's oral cavity. The cow re-chews the grass and starts over.
A sharp transition to a summer diet and overeating of juicy grass by animals lead to disruption of the pet's stomach. Stopping the mechanism of regurgitation of food is fraught with serious consequences. The remains of undigested food cause fermentation and bloating in the cow's digestive tract. Only an experienced farmer or veterinarian can save a cow from torment. Without the timely help of a specialist, a cow may die. In a severe case, the cow is given a painful procedure - a puncture of the scar.
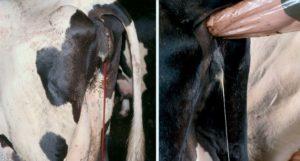
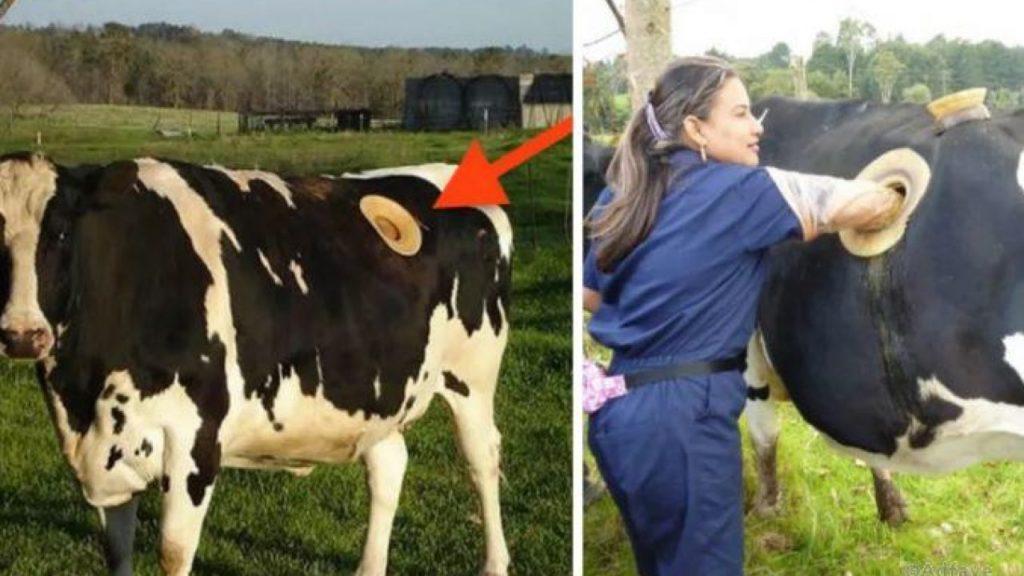
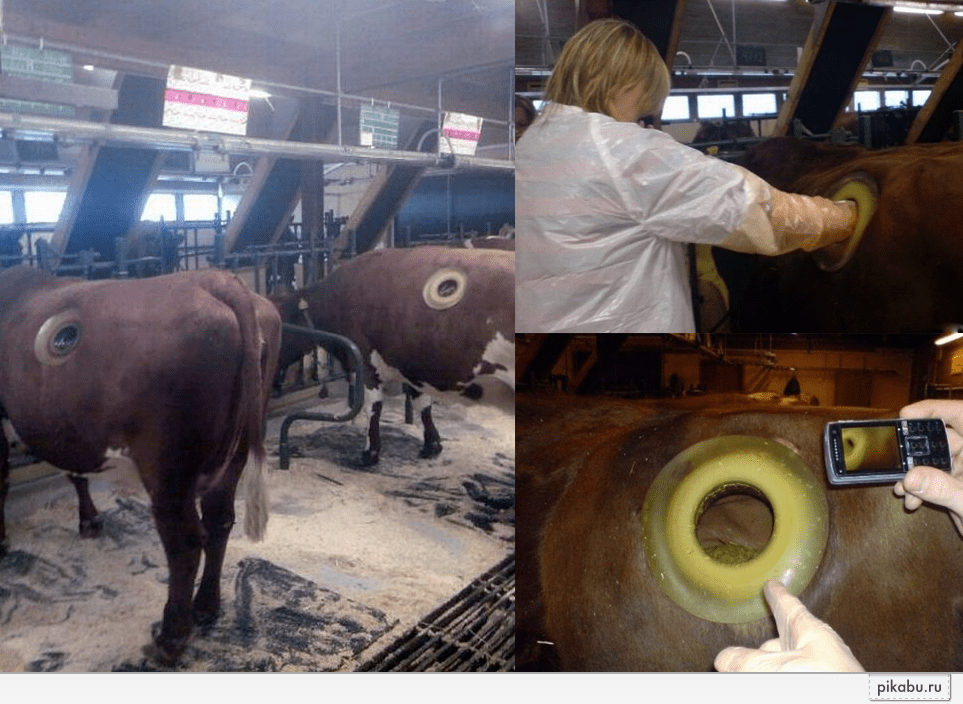
The implantation of a special fistula into the cow's body will help to simplify the task. The device is a hole made in the side of the cow. With the help of a fistula, the veterinarian gains direct access to the digestive tract of the cow. With the help of a cannula, a specialist can remove accumulated gases from the cow's intestine, remove a foreign body from the esophagus, and also directly inject a medicinal product. During the procedure, the cow does not feel pain, so the owner does not have to worry about the condition of the pet.

Getting online access
If necessary, the veterinarian will use the hole in the side of the cow for surgical treatment of the cow's vital organs. The operation is often performed on an animal with traumatic reticulitis. A dangerous disease occurs due to a sharp foreign body entering the cow's stomach. A foreign object injures the walls of the stomach, heart, respiratory organs or the internal cavity of the peritoneum.
Due to damage to internal organs, the animal develops diseases such as pleurisy, peritonitis, or traumatic pericarditis.
Under these conditions, the only chance to save the pet is surgery by opening the scar. For the convenience of surgical intervention, a cow inverter is used. Having fixed the animal, the veterinarian enters the digestive tract of the cow, removes the foreign object and, after dissecting the scar wall, proceeds to rescue the damaged organ.
Relocation of microflora
When treating acidosis (accumulation of lactic acid in the stomach) and other disorders of the digestive organs, the veterinarian resorts to transfaunation. The procedure consists in the relocation of a certain number of microorganisms from the rumen of a healthy cow into the digestive tract of a sick animal.
From a cow kept on a farm, you can safely take up to 2 liters of liquid stomach contents. A hole made in the side of the animal allows valuable microorganisms to be placed in the digestive tract of a sick cow. The procedure is carried out for 40-60 minutes. Treatment helps to improve the work of the digestive tract of the cow and restore the lost productivity of the animal.
Laboratory research and experiments
The effectiveness of diagnostic studies directly depends on the speed of the actions taken. With the help of a fistula placed in the cow's abdomen, the specialist can immediately take the necessary samples. The valve allows the specialist to determine exactly how a certain type of feed or medicinal product affects the digestion of a cow.
A few years ago, similar studies were carried out by the sounding method. The traditional diagnostic method brought physical suffering to the animals. Thanks to the modern method of research, the pet tolerates diagnostic procedures completely painlessly.

Stages of the operation
The valve is installed only for adult, well-fed, calving cows. The optimal age for the operation is 2.5-3 years. At a younger age, pets continue to grow, so the established fistula can be very displaced.
Cow preparation
Experienced people begin preparatory measures 2 weeks before the operation. Whether vaccinated or not, cows are tested for susceptibility to tuberculosis, brucellosis, anthrax and other infectious diseases. Vaccination is stopped completely 30 days before the valve is installed. Only 60 days after the operation can you return to the usual vaccination schedule for the owners. 12 hours before the start of the procedure, feed the pet is stopped.
Some experts prohibit watering cows before the operation, but the overwhelming number of veterinarians consider this measure unnecessary.
Scar surgery
As a rule, the operation is performed in autumn or spring. During this period, the weather is comfortable, and there are no annoying insects. The fistula is placed under local anesthesia. Using chalk, the veterinarian marks the place on the animal's body for the implantation of the cannula.
The device is made of special plastic. Due to its resistance to oxidation, the fistula is not destroyed by stomach acid and microorganisms. The valve should be located in the hunger fossa, to the side of the spine. The operation is carried out according to a single algorithm.
- The animal is given a muscle injection of any relaxant. This will help relieve a little nervous tension and calm the cow.
- The cow is securely fixed on a special machine.
- Burenka is injected with an anesthetic and an incision is made in the place marked with chalk.
- The veterinarian gently spreads the muscle fibers and makes an incision in the peritoneum.
- The tissues of the scar wall are carefully pulled to the incision site. Carefully, without affecting the muscles, the specialist fixes the scar tissue on the cow's skin.
- The veterinarian then makes an incision in the stomach and stitches the edges of the tissues with the cow's skin.
- The cannula is heated, this gives the part elasticity.
- The fistula is inserted into the hole made. The device securely wraps around the muscles, so there is no need to secure it.
- The hole is hermetically closed with a special lid.
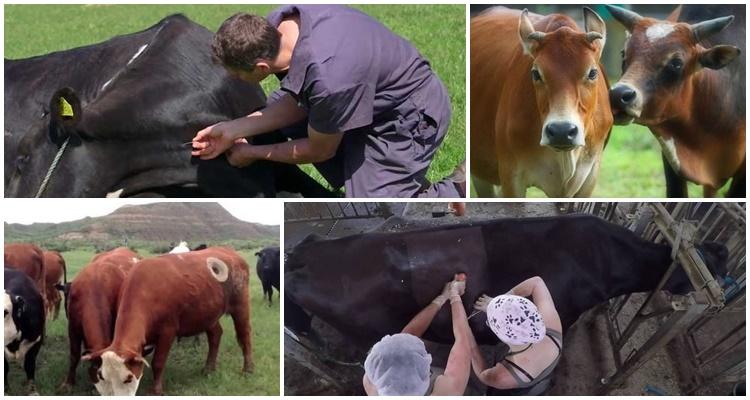

Benefits of fistula placement
Despite the frightening appearance, fistulas have a number of advantages over traditional methods of influencing the animal's body:
- Possibility of emergency intervention in a situation dangerous to the health of a cow. You can get access to the internal organs of the cow at any time.
- The possibility of urgent removal of food from the stomach of the pet. Digestive problems are often caused by poorly digested food. Urgent cleansing of the stomach of a cow from poor-quality feed will help prevent illness. The easiest way to do the procedure is through the opening valve.
- Convenience of the procedure for removing accumulated gases from the digestive tract of a cow.
- Constant control of the bacterial environment inhabiting the stomach of the cow.
- Possibility of competent preparation of the cow's diet. Thanks to the installation of a fistula, it is easy to determine which type of food is right for your pet. Ultimately, the technology helps to increase milk yield and product quality.
- Convenience of administering medications directly to the digestive tract of the pet. Thus, the chances of saving the cow in case of acute poisoning increase.
Follow-up care
During the first week after the operation, the tumor on the injured part of the body does not fall off, so the animal is given antibiotics. The course of taking the drug is designed for 5 days. All this time, the diseased area is treated with any disinfectant solution.
The cow is kept in an isolated, clean room. It is necessary to protect the pet from contact with relatives and other animals. The healing process should take place under the supervision of a specialist. The diet of the cow does not change. The milking of the animal is carried out according to the usual schedule for everyone.