Causes and symptoms of rinderpest infection, methods of treatment and prevention measures
Plague is a particularly dangerous infectious disease of zoonotic origin. It is accompanied by severe intoxication, fever, disorders of the lymphatic system, tissue necrosis. When infected with plague, the cattle mortality rate is 100%. The disease is also dangerously high contagious and rapidly spreading to all livestock. Although plague is considered an eradicated disease, every farmer should know more about it.
What is rinderpest?
In the International Classifier, plague is included in group A (carries extreme danger). The official name of the pathology is Pestis bovina. Has a viral nature of origin, destroys the mucous membranes of organs, skin. The infected areas become inflamed and die off quickly.
Cattle remains highly susceptible to the plague virus. In addition to cattle, other ungulates are also likely to get sick:
- Goats.
- Sheeps.
- Pigs.
- Wild ungulates (buffalo, deer).
The disease is caused by a paramyxavirus virus. The plague pathogen has its own RNA. When released into the bloodstream, it quickly spreads in it.
The first information about rinderpest dates back to the beginning of our era. The contagious nature was discovered in 1711, and confirmed in 1895. The causative virus was established later - in 1902. Now rinderpest is recorded only in 3 world regions: Tropical Africa, the Middle East, Asia. In the countries of the former USSR, rinderpest has not been diagnosed since 1928.
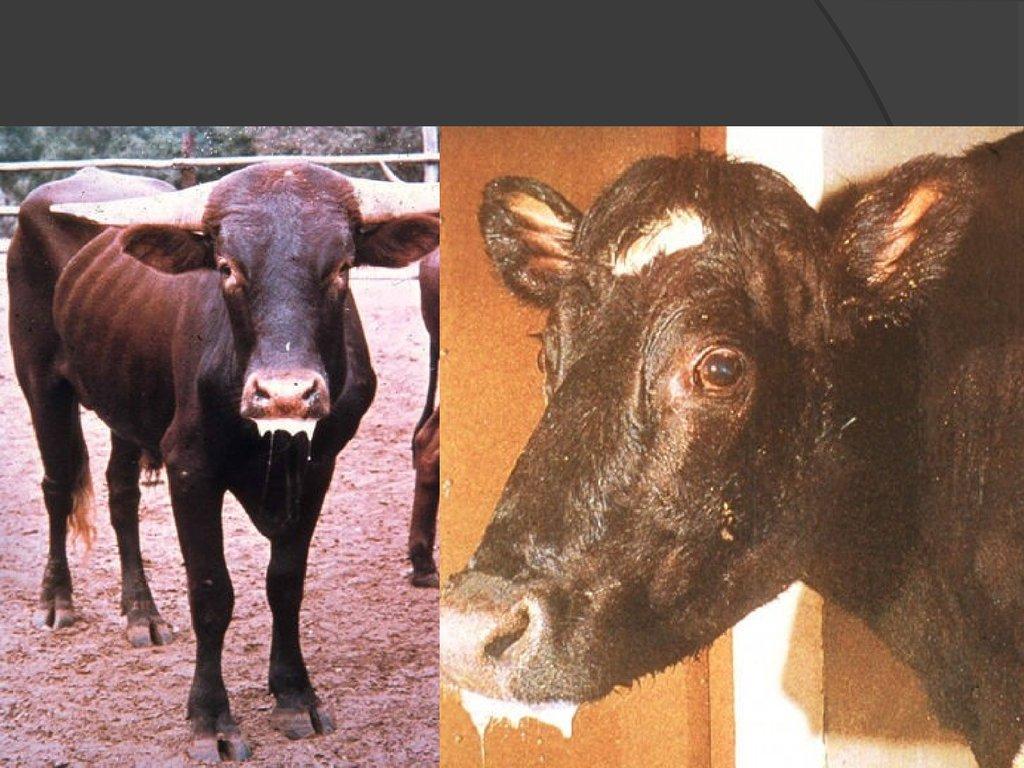

Causes of occurrence
The disease is especially contagious for young cattle up to one year old. The main source of plague transmission is the infected individual. It releases pathogens into the air that are contained in body fluids, feces, mucus. There are 3 main ways of transmission of plague:
- Through the air. The virus enters the respiratory tract of cattle with oxygen. This is facilitated by group and close housing, poor immunity of the livestock.
- Through feces (alimentary route). Virus particles are present in the secretions. They can get into food, water. This is typical for farms where sanitary standards are not observed and disinfection is not carried out.
- Fallen individuals (mechanical). Birds and insects feed on infected corpses, which, upon contact with cattle, transmit the virus to them.
The causative agent of rinderpest is transmitted through equipment, servants' clothes.No cases of transmission from mosquitoes, ticks, horseflies were recorded. The pathogen remains viable on the skin, horns and meat of dead individuals for up to a month. Therefore, the infected corpses must be burned.
Symptoms of the disease
The incubation period for rinderpest is from 3 to 7 days. There are several variations in the manifestation of infection: typical, latent or abortive (does not reach full development, stops at an early stage). Symptoms vary depending on the species, breed and immunity of the cattle.
The plague is most pronounced in young animals. The development and progression of the disease takes place in 3 stages.
Stage one
Begins in cattle immediately after the end of the incubation period. The second name is febrile plague. Duration - no more than 2-3 days. The following clinical signs are characteristic of cattle:
- Rapid breathing, fast pulse.
- A sharp jump in temperature up to 40.
- Complete refusal to eat at the same time as excessive consumption of water.
- Redness and inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye.
- Acquiring high sensitivity to daylight.
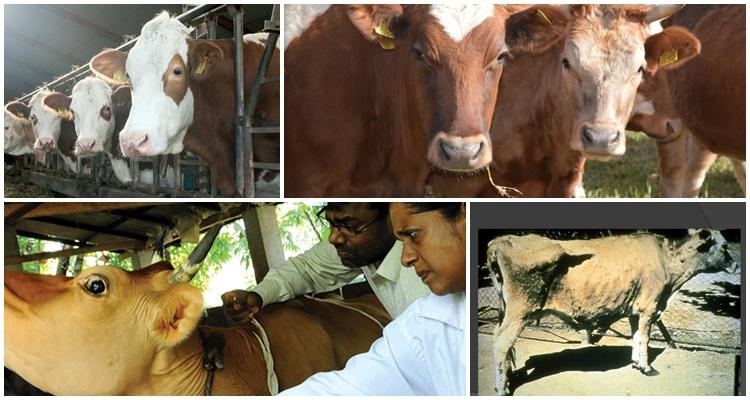

Stage two
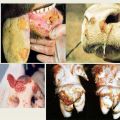
Begins after 2-3 days of primary leaks. An indicator of the second stage of plague in cattle is the appearance of necrotic foci on the mucous membranes. The conjunctiva, mouth and nasal cavity are primarily affected. Pregnant individuals die at this stage. Symptoms of the plague in the second stage:
- Restless behavior - individuals sneeze, turn their heads, tread on the spot.
- Rapid progression of serous conjunctivitis, eventually turning into purulent.
- Profuse discharge of purulent exudate from the nasal passages. Scabs of dried pus appear on the nostrils.
- Severe swelling of the nasal mucosa, eyes.
- Increased salivation. At the same time, saliva is foamy, contains blood inclusions.
Third stage
At this stage of the progression of the plague, serious disorders of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract occur. Cattle have persistent diarrhea or involuntary stool. The masses contain blood, mucus, particles of dead intestines. The mucous membrane protrudes in the anal area. The act of defecation is accompanied by pain, to relieve it, the animal arches its back.
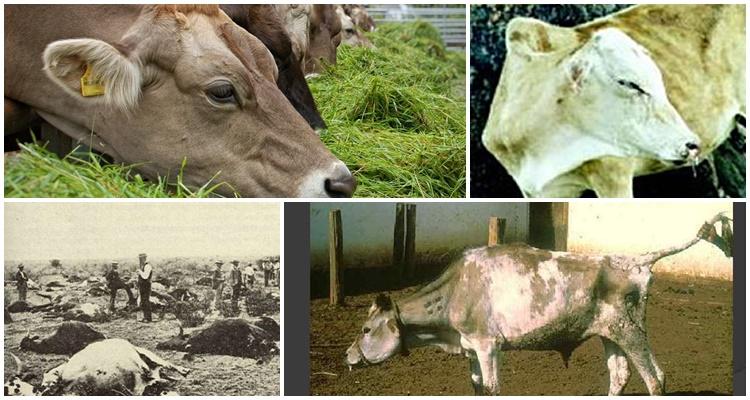

Such a disorder leads to rapid depletion and dehydration of the cattle body. There is a sharp weight loss, breathing problems appear: painful cough, pulmonary emphysema. At the same time, the temperature remains normal or falls below normal. Death occurs by 8-9 days after the first symptoms of plague.
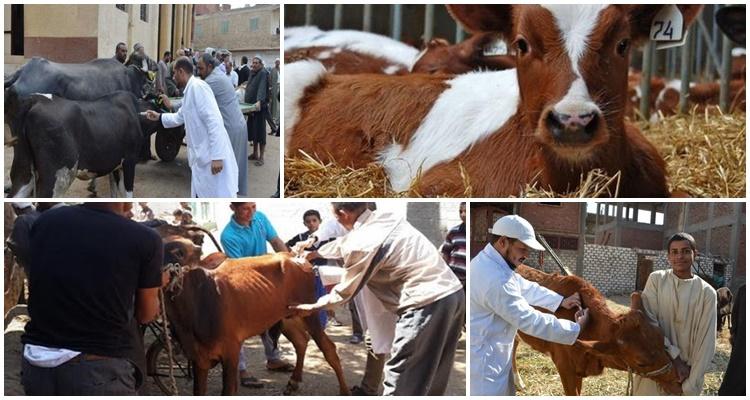
Plague diagnosis
The clinical manifestation of plague in cattle is similar to those of other infectious pathologies. The diagnosis cannot be made based on symptoms and condition alone. For an accurate result, laboratory diagnostics are carried out. In live individuals, this is a blood test. The procedure can take place in 3 ways - detection of specific antibodies, changes in the structure of cells, enzyme immunoassay. For dead animals, postmortem examination is carried out. In laboratory conditions, particles of the spleen and liver, lymph nodes are studied. Tissues are taken from dead individuals no later than 5-6 hours after death. The presence of the plague pathogen is indicated by changes in the internal organs of cattle:
- Thickening of the small intestine.
- Ulcers, hemorrhages in the intestines.
- Enlarged and inflamed lymph nodes.
- Curdled sediment on all mucous membranes.

Pathology treatment methods
Any measures for treating rinderpest are prohibited at the legislative level. All infected animals are killed in a bloodless manner. Then the carcasses are completely burned. Premises and instruments are subject to thorough two-fold disinfection.
When plague is detected in cattle, the farm is closed for quarantine, and the settlement is transferred to a quarantine regime. It includes a ban on the export / import of animals, dairy and meat products, skins, feed. The movement of people outside the village / city is restricted.Other actions are also carried out:
- Complete exclusion of grazing.
- The cattle-breeding premises are subject to daily cleaning. After it is treated with caustic soda.
- All cattle in the village are vaccinated.
If quarantine restrictions do not bring results, the administration of the settlement decides to slaughter the entire livestock. Then the places of detention are cleaned and disinfected. With positive dynamics, the quarantine is extended for another 21 days. After that, several young heads are launched into the barn, observed for 3 months. If no signs of plague are found, the launch and breeding of new individuals is allowed.
Prevention methods
A specific measure for the prevention of plague is periodic vaccination of cattle. Preparations from a deactivated or live culture of the pathogen are used. It is performed as a subcutaneous injection. The acquired immunity lasts for 3 years.
Other preventive measures include typical antiepizootic actions. This is regular cleaning in places of detention and periodic disinfection with chemical. reagents. Stalls and sheds should be well ventilated.
Close housing is prohibited: one cow needs at least 7-8 sq. m. The diet of cattle should be balanced and rich in vitamins.
Rinderpest is considered a completely eradicated disease in Europe, America, Australia. But, given the real damage and the danger of this pathology, it cannot be discounted. Every farmer should know the typical clinical picture of plague in order to recognize the disease in time. Preventive measures should not be weakened either, since this is a reliable protection against such infectious pathologies.