Symptoms and signs of rabies in cattle, treatment methods and vaccination regimens
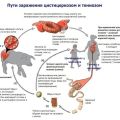
Rabies is a deadly viral disease that occurs in wild and domestic animals, when in contact with them (bite) and if the saliva of a sick animal gets into the wound, the virus is transmitted to humans. The source of the disease is often cats, dogs, foxes, bats and ordinary mice, from which cows (cattle) become infected with rabies. What actions are required when a virus is detected on the farm, how to prevent its appearance, this is today's conversation.
Causes of the disease
The disease develops after the Neuroryctes rabid virus enters the body of an animal. A cow can be bitten by an infected mouse, sick dog, fox or other wild animal, then the virus enters the wound along with the carrier's saliva.
Another way to get infected is through contaminated feed, such as hay that has been spilled with the saliva of a sick animal, or lumps of salt in the barn. This happens if purchased infected animals enter the farm.
The virus has a bullet-like shape, its highest concentration is found in saliva, tears, cerebral cortex, ammonium horns of sick animals. It is well preserved at low temperatures, when boiled, it dies instantly, in unused corpses of sick animals it can be stored for years. After infection, the virus enters the spleen of the animal, from there it enters the central nervous system, and affects the brain.
Animal rabies was described by Democrides and Aristotle even before our era. For many years of studying rabies, they did not manage to defeat it, the disease remains fatal for animals and humans. The only way to combat it is through vaccination. Rabies is found all over the world, except for Antarctica and island states (Japan, New Zealand).
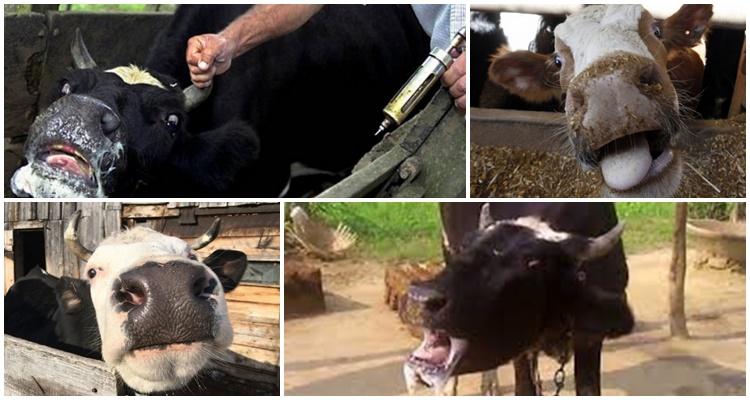

Signs and symptoms of rabies
Rabies affects the central nervous system of animals. Infected cows become lethargic and lethargic or overly agitated. The subsequent stages of the development of the disease are characterized by hydrophobia, increased salivation, and self-gnawing. Distinguish between violent and calm forms of cattle rabies.
Exuberant form
In this form of rabies, animals are highly agitated. Cows behave atypically:
- become aggressive, jump, bang their head against the walls;
- roar loudly, can attack other animals;
- trying to comb or gnaw the place where the virus entered (bite);
- shortness of breath and photophobia occurs.
The next stage in the development of rabies in cows causes paralysis of the lower jaw and respiratory organs. Then the legs fail. The animal stops swallowing and moving. Complete paralysis sets in.
Calm
This course of the disease is more typical for cattle. In a calm form of rabies, the following symptoms appear:
- animals are lethargic, apathetic;
- cows lose their appetite;
- weight decreases sharply;
- gum is lost;
- photophobia arises, animals try to hide in a dark corner.
The next phase of development of rabies is characterized by the development of paralysis of the lower jaw (mouth opens, tongue falls out). The cow stops chewing and swallowing food, refuses food and water. Complete paralysis and death of the animal sets in. The incubation period of rabies in cows can last from 2 to 12 months, the acute phase of the disease - 5-7 days.

Diagnostics
If the animal's behavior seems strange, you should separate it from the rest of the livestock and call the veterinarian. If the veterinarian detects signs of the disease, the head of the animal is sent for analysis. It is carefully packed in 5-6 layers of polyethylene and immediately taken for diagnostics. In the laboratory, a study of the cow's brain is performed.
The result is immediately reported to the head of the district and the chief sanitary doctor. Upon confirmation of the diagnosis, the farm and the area where it is located is immediately quarantined. Animals that do not have obvious signs, but may be sick, are necessarily isolated. They are examined by a veterinarian 3 times a day. Healthy livestock are examined by a veterinarian every 3 days for new cases of disease.
The barn is treated with a solution of formaldehyde or caustic soda. Manure is carefully removed, litter is burned, feed from feeders, salt and chalk in the barn are destroyed. Feeders and drinkers are disinfected. Other animals on the farm (cats, dogs) are examined and vaccinated.
The things of farm workers (gowns, gloves) are disposed of, which could get saliva from sick animals. In case of suspicion of the possibility of infection, vaccinations for farm employees are mandatory.
Important: the saliva of an infected animal can enter the human body through wounds, scrapes and cuts on the hands. The quarantine is lifted 60 days after the last case was discovered.
Is it possible to cure and what to do with corpses
Rabies causes 100% mortality in animals. Treatment is not carried out due to inefficiency, sick cows are destroyed, milk is completely utilized, the corpses of cows are burned, processed into meat and bone meal, disposal in cattle burials is allowed. Healthy animals (all available livestock, cats, dogs, other animals) are revaccinated.
Is it possible to eat the meat of sick animals for food
When a diagnosis is made - rabies - the area in which the disease is detected is quarantined. Animals are not brought in or taken out from the area. Milk, meat, skins of sick animals are completely burned. Do not eat meat, drink milk, even after heat treatment.

The meat of vaccinated animals that have a suspicion of rabies, but the diagnosis is not confirmed, can be eaten, the animal is examined by a veterinarian before slaughter and a certificate of the animal's condition is issued.
Vaccination schedule
The first rabies vaccination is given to calves 6 months of age, then the vaccine is repeated every 2 years. In case of a difficult epidemiological situation in the area, calves are vaccinated from 3 months. Vaccination is done during the dry period, when the cows do not give milk. Weakened, sick animals are not vaccinated.Cows are not given the vaccine.
The vial with the vaccine is shaken to stir, after opening it, the vaccine is completely used. A cow is injected intramuscularly with 1 milliliter of the drug. The vaccine should not be frozen. In case of accidental violation of the tightness of the bottle, it is poured with boiling water and boiled for 7-10 minutes to completely destroy the virus. Vaccination is done with sterile disposable syringes, the vaccination site is disinfected with alcohol. Vaccinations are performed by veterinarians. Vaccination documents are kept by the farmer and the district health officer.
Other prevention measures
In order to prevent the spread of rabies among the livestock of cattle, it is necessary to monitor the state of morbidity in the area where the farm is located. Destroy wild animals that have spawned. Protect the herd from the attack of wild animals, fence off the walking areas. Vaccination against rabies in domestic animals (dogs, cats). To vaccinate a healthy livestock of cattle, calves. Timely vaccination of animals, preventive measures taken in the farm allow to avoid massive infection of animals and save the livestock.