Names of inexpensive but effective drugs for treating bovine actinomycosis
Actinomycosis most often affects cattle. This is a disease of a fungal nature, with which animals fall ill more often in autumn and winter during stall keeping. It is characterized by the formation of tumors at the lesion sites. Consider the forms and symptoms of cattle actinomycosis, treatment with inexpensive but effective drugs, diagnosis and preventive measures.
Where does the disease come from?
In cows, actinomycosis affects the lower jaw, head, neck, bones, lymph nodes, tongue and oral cavity, udder. The causative agents are Actinomyces bovis fungi. They are common in nature; livestock can become infected when grazing or eating hay or straw from cereals.
Fungi enter the body of cows through sick teeth, microtrauma on the mucous membranes of the mouth and digestive tract, skin, nipples. In practice, it has been established that at home an animal can become infected when eating roughage (sharp stems injure the tongue or mouth, fungus penetrates through the wounds). Fungus is especially dangerous for the calf during the period when teeth begin to grow.
At the site of the introduction of the fungus, an inflammatory process begins, a granuloma grows. In the center of formation, the tissues are necrotic, then fibrous tissue appears. The disease progresses, the abscesses open up and form fistulas that do not heal for a long time. The fungus also affects nearby tissues, which forms a scar. The pathogen can penetrate into the blood vessels, with the blood it spreads throughout the body, including bone tissue, and forms new lesions.

Symptoms
What symptoms actinomycosis manifests itself depends on the place of introduction of the fungus, the ability of the bovine body to resist infection. The general symptom is the formation of actinomics in the form of dense, painless, but spreading tumors.
Head and neck involvement
Actinomycomas can be located on the lower jaw, on the cheek, on the cheekbone, on the neck near the larynx. The bumps eventually break through (outward or inward), pus flows from them, blood can be mixed into it. If actinomycomas are located on the lower jaw, the animal's muzzle can swell and teeth fall out, saliva flows from the mouth.
If tumors have formed on the tongue, it swells, "stiffens" and falls out of the mouth. With the defeat of the mouth and gums of the tongue, the cow cannot eat and loses weight, although she does not lose her appetite. This leads to a decrease in productivity.
Lymph node involvement
An encapsulated abscess forms in the cow's lymph nodes affected by the fungus.Actinomycetes affect the submandibular, buccal and cervical lymph nodes. The tumors are dense, over time, fistulas form from them with the release of pus when an infection is attached.
In some animals, lymph node growths can dissolve, and there is a temporary improvement, but then the actinomycosis comes back again. After the abscess is opened, the animal may have an increase in temperature for a while, the site of the lesion may swell.
Actinomycosis of the udder
Tumors ranging in size from beans to eggs are localized under the skin of the organ or in the depths of the lobes, more often the back. They open either outward or into the milk passages. In this case, their contents end up in milk. You can't drink it. The tumor is dense, painless, grows rapidly and can reach large sizes.
Generalized form
It is rarely observed in cows. In this case, various internal organs are affected - the liver, kidneys, lungs, gastrointestinal tract, ureter.

How is actinomycosis diagnosed?
It is impossible not to notice the tumors, at least those located under the skin, since they are not small in size. But, in order to accurately determine actinomycosis, a diagnosis is needed. For analysis, take pus from the fistula, granuloma tissue, sputum, urine, make a biopsy for histological examination. Actinomycosis is differentiated from actinobacillosis, since the diseases are similar in symptoms and nature of the course. The difference between them is that in the first case, the lesion is more often on the bones, in the second - on the soft tissues. Fungal actinomycosis should be distinguished from tuberculosis, osteomyelitis, and simple abscesses.
Treatment and prevention methods
Actinomycomas are painless and therefore do not cause discomfort in cows, except for those located in the oral cavity. But this does not mean that nothing needs to be done. Most animals will not recover on their own and therefore need treatment. The therapy should be carried out by a veterinarian, it will be difficult to do it yourself. The prognosis of treatment in most cases is favorable if only soft tissues are affected, if bones and internal organs are affected, treatment may be ineffective.
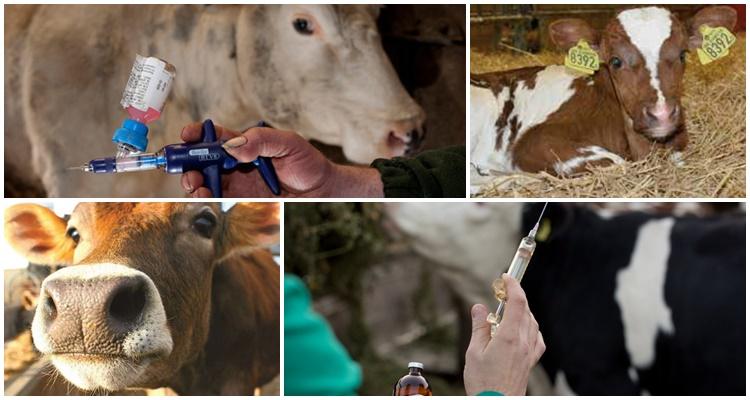

Providing first aid
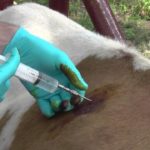
Before starting treatment, remove the cow from the common herd and put it in a separate stall. It should be dry and clean. Treat the edema with a solution of iodine or antiseptics. You don't need to do anything else.
Health care
At the beginning of the disease, iodine preparations ("Iodinol", iodine solution, potassium iodide) are used, they are given orally and injected into the seals. If the tumor is pronounced and has been developing for a long time, intravenous fluids will be required. A good effect is given by antibiotic therapy: Oxytetracycline is injected into the formations of a bull or cow every day, the course of treatment is 4-6 days, or Polymyxin is injected once every 1.5 weeks. Usually, during this time, the neoplasms have time to dissolve. In severe cases, "Benzylpenicillin" is used (for animals that are not allergic to the drug). It is important to complete the course of therapy, even if the tumors seem to have disappeared.
If a band of tumors has become inflamed, after antibiotic therapy with the use of "Erythromycin", "Levomycetin", "Tetracycline", they are used for excision together with capsules. In case of relapses, re-intervention will be required.
After therapy, you need to wait 3-5 weeks, if the actinomycosis does not return, we can assume that it has been defeated.
Preventive actions
The stalls of sick animals are disinfected with a 2-3% solution of caustic alkali or slaked lime.Preventive measures: cows should not be grazed in areas with outbreaks of actinomycosis, on damp pastures. If possible, steam the roughage so that the stems become softer. So there is a chance that the animal will not prick the tongue, gums or mucous membranes and become infected. Plus exposure to temperature will reduce the number of pathogens, and not only actinomycetes, but many others.
Actinomycosis of cows is a dangerous infectious disease that affects cattle during the stall period. Animals become infected when eating hay and straw, on which there is a pathogen - a fungus. Antibiotic treatment and surgery are usually effective, but not too advanced. Therefore, you need to monitor the animals, and at the first suspicious signs, contact your veterinarian. The drugs used for the treatment are available and cheap and can be purchased at any pharmacy.