What factors affect milk production in cows and methods of determination
The performance of dairy cows is measured in terms of the amount of milk produced during the lactation period. The lactation capacity of cows is divided into four types of productivity: consistently high, not consistently high, rapidly declining and consistently low. The method by which milk yield is determined in cows consists in control measurements of milk yield.
How to determine the milk production of a cow
The average duration of a cow's lactation is 240 days. Productivity is assessed by milk yield for the general period or its individual segments. The method of assessment for complete lactation is used more often. Control measurements are made every 10 days, and then the average is calculated. A less accurate way of measuring is by the highest milk yield per day. The resulting figure is multiplied by the number of days, which is the duration of lactation.
In dairy and mixed breeds, milkiness is always higher than in meat breeds. Maximum productivity is observed within two months after calving. The relationship between the milk production of cows and the duration of their lactation in the breeding farm is shown in the table:
| Lactation | The first | The second | Third | Fourth | |
| Milk yield (in kilograms) | 305 days | 9091 | 9091 | 9078 | 8789 |
| 365 days | 10507 | 10879 | 10864 | 10518 | |
The ability of a cow to lactate is shaped by the interaction of heredity and housing conditions. Fat content, protein content in milk is also inherited. But with favorable or unfavorable external factors, the inherited qualities improve or worsen.

Factors affecting productivity
The milk yield and milk quality are influenced by the breed, physiological characteristics, indoor microclimate and animal diet. Early milk production in breeding is beneficial, as it presumably leads to increased economic benefits and a quick return on the cost of raising animals. But often record rates are achieved due to individual characteristics, and not early insemination and lactation.
Breeds of cows
Milk fat indexes differ depending on the direction of the breed:
- milk - 3.5-3.8 percent fat, productivity - 5000-7000 liters per year;
- mixed - fat content 3.8-4 percent, volume per year is 4500-5500 liters;
- meat - fat content reaches 4.5 percent, productivity - 1200-2000 liters of milk per year.
Low milk production of beef cows is due to physiological characteristics. They have small udders, only for feeding calves, short lactation period.But milk has the highest fat content.
Age of animals
Milk production rises up to four to five years and decreases after six. For the first time a cow calves at two years old. Milk content in the first lactation is 80 percent. At four years old, it reaches one hundred percent. By the age of eight, productivity declines by 6 percent.
Live weight of cows
The milk yield is influenced by the weight of the cow. The average weight of dairy cattle during the first lactation should be 400 kilograms. With age, the mass can increase and be 500 kilograms. But the large body weight of first-calf heifers does not affect the amount of milk yield after calving. The influence of the weight category is interrelated with the selection of heifers by weight for the first mating. Also, the selection criterion for insemination is high growth.

Feeding and maintenance
During pregnancy, start-up and in the first months of lactation, the cow needs a balanced diet rich in proteins and calcium. The animal's body receives enough energy. As a result, milk contains more protein and fat. Feeding silage and fresh hay during deadwood increases productivity.
Physiological factors are interrelated. Normal weight for insemination and lactation is achieved through good nutrition of the calves. Correct feeding develops the stomach, so animals absorb more food, quickly gain the necessary mass and show high milk productivity.
Milk production is influenced by the way cattle are kept. Tied cows consume less feed and produce more milk. Increased humidity and lack of movement in stall housing will reduce productivity. The best performance is observed in cows in pasture or stall-pasture housing.
Timing of the first insemination
Cows become sexually mature at 10 months. But the sixteenth month is considered a favorable time for insemination. At an earlier age, there are difficulties with bearing a fetus and childbirth. As a result, the first lactation is low and may be accompanied by a delay in the placenta.
Mating readiness also depends on the weight of the cow. In case of a shortage of mass, insemination is postponed to a later date.
Deadwood duration
To maintain high milk yields, milking must be stopped before calving. In earlier calving cows, the start-up begins 50 days before calving, in first-calf heifers - 60 days. The absence of a dry period depletes the cow's body. As a result, after calving, milk yield is reduced by 25-40 percent. Too long dead wood reduces productivity by 15 percent.

Calving season
With grazing, calves are born in spring. In summer, animals feed on fresh grass and receive the necessary vitamins. Also milk yield increases after winter calving. With stall keeping, calves are born within a year. Such an organization of the vital activity of animals is associated with a lack of space for keeping a large number of newborns. Also, it is impossible to stop the conveyor production of milk and provide all livestock with a dry period.
The productivity of cows at breeding farms remains at the same level throughout the year and slightly decreases in winter. To maintain high milk yield, the animals are given nutritious food all year round, adhere to the mating and calving schedule.
Health
Diseases that reduce milk yield:
- limb injuries;
- reproductive disorders;
- tuberculosis;
- mastitis.
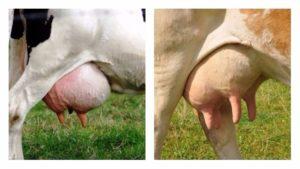
Loss of milk production due to untreated pathologies is 10-50 percent. Most often, mastitis leads to a decrease in milk production. The disease occurs when a bacterial infection is contracted as a result of improper milking and unfavorable conditions.Milk of mastitis cows is not suitable for human and animal consumption due to the content of impurities and bacteria. But milking is not stopped, because then it is very difficult to milk the cow again.
Razda
Lactation is increased in various ways. Section includes the correct organization of animal life throughout the year:
- raising calves;
- preparation of first-calf heifers for childbirth;
- adherence to the schedule and norms of the diet during pregnancy and after childbirth;
- correct milking technique.
The cow begins to distribute on the fourteenth day after calving and is carried out for one hundred days. At this time, the animal is given more food. Admission is called advance payment. It is used as long as there is an increase in milk yield. Then the addition to the main diet is gradually canceled.
Conditions of detention
Stable animals must be provided with a comfortable microclimate. Milk yield is negatively affected by drafts, noise and moisture. Communication also affects milk production. Cows that see each other and communicate give more milk. On foreign farms, music is played during milking. Contemporary and classical music also increases milk production.
Care
Low milk yield is observed in animals that are rarely cleaned. Before and after milking, the udders should be washed with warm water. Milk-covered teats collect bacteria from dirty litter. As a result, mastitis develops. A clean stall, a clean udder and a clean milkmaid's hands increase milk volume. Animals should be taken for a walk. The best option for keeping is free grazing in summer and stall keeping with short walks in winter.
Milking quantity
The udder is a parenchymal organ that continuously produces milk. Fluid builds up and presses on the inner tissues. When the chambers of the udder are full, milk production stops and it is sucked back.

The volume of production is affected by the capacity of the udder. In beef breeds, it is small, so the frequency of milking has little effect on the amount of milk. It is recommended to milk dairy cows 2-3 times a day or more often, but at regular intervals. The number of milkings can be increased, but not decreased. Otherwise, the milk volume is reduced by 15 percent. With an annual productivity of more than two thousand liters, switching to two-time milking increases the volume of milk by 10 percent.
Milking frequency does not always need to be increased. Performance records were recorded with two milking a day. It is important to follow technique when expressing milk by hand. Gentle massage movements improve blood circulation and milk flow in the udder, promote complete emptying.
Features of animals
The duration of the lactation period and milk production are individual for each cow and may differ in animals of the same breed under the same conditions. The response to the frequency of milking depends on individual characteristics.
The amount of milk is influenced by the shape of the udder and the rate of milk flow. Milk is quickly expressed by the apparatus in cows with rounded cup-shaped udders or with an elongated tub-shaped udder. Animals with a goat and a primitive udder shape are milked by hand due to low milk yield.
Heredity, housing conditions, rearing characteristics and breeds have a greater or lesser impact on milk production in different herds. Therefore, in order to increase milk yield, it is necessary to study the relationship between external and internal factors in each specific farm.