Rules for breeding and keeping rabbits in Siberia, the choice of breed and what to feed
The rabbit organism is quite resistant to adverse weather conditions, but still not adapted to the extreme cold and winds observed in the Siberian regions. Therefore, breeding and keeping rabbits in Siberia requires a special approach: the construction of a closed insulated rabbitry, the use of high-calorie feed. Siberian farmers are trying to acquire more hardy, cold-resistant breeds.
Features of the region
The territory of Siberia lies in the temperate continental and subarctic climatic zones. The weather conditions are harsh here: abundant precipitation and strong winds. In the wild nature of Siberia, the rabbit will not survive even without taking into account the predators: it will simply die from the cold in early November.
Rabbit breeding in this climate is more costly, but still profitable. The female gives birth to 25-30 rabbits per year, as a result, the owner receives 40-50 kg of annual slaughter weight. An additional source of income is the sale of skins. Rabbit fur is used for sewing winter haberdashery and footwear.
Farmers of Irkutsk, Novosibirsk, Omsk regions are engaged in rabbit breeding. The largest and most successful farms are Siberian Rabbit (Krasnoyarsk) and Tatianin Khutor (Novosibirsk).
Breed selection
Suitable for growing in Siberia are hardy, disease-resistant breeds, characterized by voluminous and dense wool that reliably keeps warm. Most of these breeds are bred in Russia. Russian rabbits are able to survive in winter even with open cages. But to preserve the health of animals, it is better to build a closed rabbitry. In Siberia, rabbits can be raised to obtain both dietary meat and valuable fur.
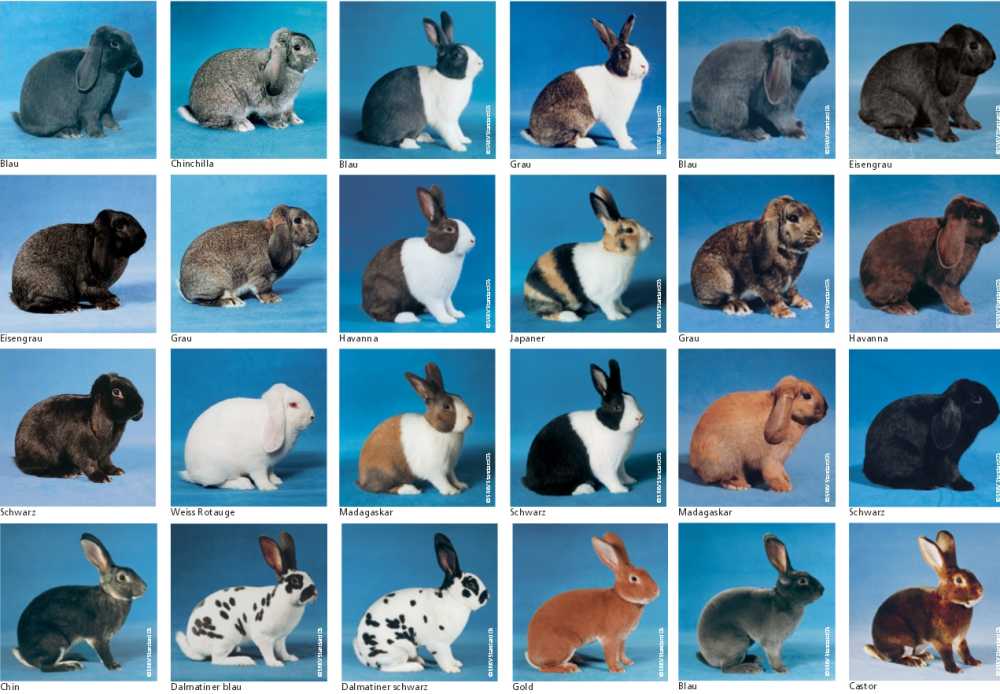

For meat
Meat rabbits are distinguished by their massive physique, rapid growth of muscle mass. Farmers in Siberia should pay attention to the following breeds:
- Californian is a breed that has gained popularity for its rapid growth. By the age of 5 months, the animal reaches 5.5 kg, subject to slaughter. Females are fertile; they bear 8-10 rabbits. The soles of the paws are covered with thick wool, so the cold mesh coating does not cause discomfort.
- New Zealand Red is the ideal breed for cages. Strong, heavy, well-fed rabbits reach 4.5 kg by 5 months. The fur on the soles keeps the paws from freezing on the mesh floor. Harsh climatic conditions do not care, but the breed is sensitive to drafts.
- The gray giant is a hardy, unpretentious, fast growing rabbit with impressive dimensions. By the age of 5 months it reaches 6 kg.
On skins
The body size of these rabbits is small, but the fur is of high quality. The climate of Siberia is optimal for fur rabbit breeding.Rabbit fur in warm and humid conditions has a short operational life, and when raising animals in Siberia, it does not lose quality for 3-4 years, and is not inferior to mink fur in terms of wear.
Farmers in Siberia should purchase the following breeds:
- The white giant is a large rabbit weighing up to 5.5 kg. It develops slowly, reaches maturity only by 7 months, but it has a luxurious snow-white coat. Therefore, the breed is used mainly for obtaining fur, although meat production is also quite profitable.
- The black-brown Kazan rabbit has an unusually dense coat, reaching 24 thousand hairs per 1 cm2, and a unique coloration reminiscent of the coat of a black fox. The hairs are transversely divided: the base is brown, the tips are black.
- The Russian ermine is a small rabbit of English origin, weighing 4 kg. The color of the valuable rabbit fur resembles the white ermine coat with black spots.

For meat and fur
Rabbits of this type are less massive than meat relatives, but they have a high-quality coat, which is appreciated in the market.
Suitable for growing in Siberia:
- The Soviet chinchilla is an ideal breed for a Siberian farm, resistant to severe frosts. Pets grow quickly, are not capricious, by 6 months they reach 4.5 kg. Rabbits give birth to 8-10 cubs.
- Rex is a French rabbit with a luxurious, softly iridescent coat suitable for imitation of expensive fur. A mature individual weighs 4.5-5.5 kg.
- The Vienna Blue is an Austrian rabbit with excellent climate adaptability. Early maturity is low, but fertility reaches 8-10 young rabbits at a time. The wool is unusually soft, voluminous, 1 cm2 the body fits 21 thousand hairs.
- Silver - a rabbit with a beautiful, very dense coat. Weighs 5-6 kg. Dark gray and white hairs grow in intermixture, creating a silvery hue. The fur is so decorative that it doesn't have to be dyed.
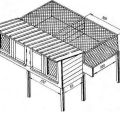
How to keep rabbits in Siberia
Rabbits live in Siberia in cages, inside insulated rabbitries, equipped with a paddock for walking. When the temperature outside is minus 30 ° C, it should be at least +5 ° C in the barn. In winter, the heating system is turned on, the optimum temperature is about +15 ° C.
Some farmers don't clean their cages until the spring thaw, and in vain. In winter, the ventilation of the closed rabbitry is reduced, and the decaying manure fills the air with ammonia, making it more moist. As a result, the rabbits develop fatal lung diseases, including pneumonia.
In Siberia, rabbits can be bred in pits. It is necessary to dig a hole 1.5 m deep, with an area of 2 × 2 m. Dig holes in the walls where the pets will breed. The pit dwelling is regularly cleaned of dirt and manure. For the winter they are well insulated, covered with insulating material so that the animals breathe.
What to feed?
The diet of rabbits bred in Siberia differs little from the diet of southern relatives. However, in the winter months, when the animal spends more energy to maintain body temperature, the diet should be more nutritious, especially if the breed is meat. A balanced diet consists of:
- fresh grass (in summer), hay (in winter);
- wood twigs;
- grains (preferably barley);
- root crops - potatoes, beets, carrots;
- compound feed;
- salt.
In winter, pets are given more hay. And they put it in the trough in small portions so that the food does not stale. Individuals selected for slaughter are given concentrates: grain, meal, cake, bone meal.
Breeding rules
In Siberia, rabbits are bred according to slightly different rules than in the southern regions, while taking into account the breed, the purpose of growing and material capabilities:
- set up a rabbitry on a hill;
- make the building of durable wood, the inner walls are upholstered with metal plates, the outside is covered with insulating material;
- do not allow drafts and sudden temperature changes, otherwise the young will die;
- install a heating system or connect the rabbitry to central heating;
- maintain the temperature in the rabbit dwelling from +10 to +20 ° C, humidity 70%;
- provide animals with constant access to feed;
- produce interbreeding to improve the health of the offspring;
- the babies are left with their mother for longer to increase their chance of survival.
Farmers note that the main problem of rabbits breeding in Siberia is not so much the high mortality of rabbits born in winter, as the refusal of rabbits to breed in winter. This is easy to explain: females intuitively understand that the offspring have a negligible chance of surviving in harsh winter conditions, so they drive away the male, and when forced mating, they refuse to feed the cubs, throw them out of the nest into the cold.
Such a nuisance is unlikely to happen if you insulate and modernize the rabbitry as much as possible so that the animals feel comfortable in it in any weather.