Symptoms and methods of treatment for lichen in goats, methods of prevention
Goats are one of the most common farm animals, domesticated by mankind since time immemorial. They are distinguished by good health, fertility, they bring dietary meat, healthful milk, wool. These animals are useful in household plots, are reared industrially, so the appearance of diseases can threaten livestock. It is important to know the causes of shingles in goats and be able to effectively cope with the disease.
Causes of the disease
Animals suffer from various types of skin infections caused by fungi. Ringworm is more common. Pets and farm animals are ill with it. More than others, cats and dogs are susceptible to this, cattle, sheep and goats suffer from it less often.
However, fungal infections are highly contagious, that is, they are transmitted by contact with an infected subject. The disease can also migrate from goats and other representatives to humans and vice versa, since there are no specific pathogens that are different for humans and animals.
Trichophytosis, microsporia and scab are provoked by the fungi Trichophyton, Microsporum and Epidermophyton. In goats, they settle on the skin and damage tissues and wool, localizing in delicate areas - ears, nose, face, abdomen, then spreading throughout the body.
Infection symptoms
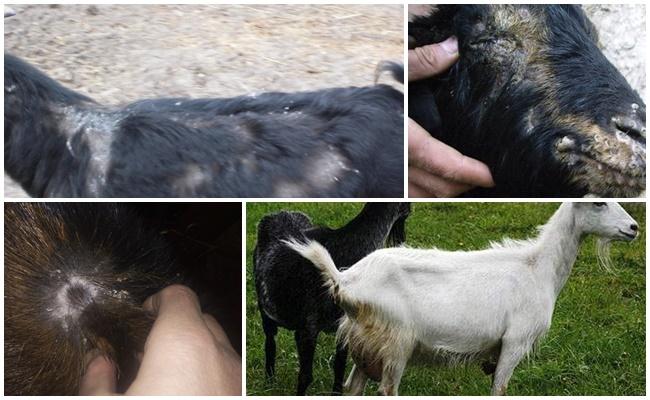
Lichen looks like a whitish, pinkish or reddish spot, often oval or round in shape, on which the coat falls out, and flaky and itchy scales are formed.

Children and young animals are more often affected, because their immunity has not yet fully formed, and the skin is much more susceptible to infections. However, this does not mean that an adult goat cannot become infected. If she comes into contact with sick fellow tribesmen or other inhabitants of the barnyard, pets, she can get sick at any age.
Initially, subtle marks of lichen can grow and grow, disturbing itching and irritation. Goats will try to scratch the affected area, which can spread the infection to other parts of the body, as well as lead to the appearance of a secondary bacterial infection due to the ingress of microorganisms into damaged tissues.
Diagnostic methods
A fungal infection can be detected visually if the disease has gone far. However, a number of infections occur in a latent form, and the external manifestations can be similar to each other. Therefore, the only accurate way to detect lichen can be a special diagnosis by a veterinarian.
For this, a smear is taken from the focus of pathological activity and examined under a microscope.If this method does not work either, you will have to use the inoculation of the pathogen on a nutrient medium in a Petri dish. This method will allow you to accurately find out the type of pathogen and start professional treatment.
How to properly treat lichen in goats
Fungal diseases are spread by spores that “cling” to the coat and attach to tissues. Therefore, before starting treatment, it is advisable to remove the hair, at least on the affected parts, as short as possible, or at least to cut it. This will reduce the risk of lichen spreading to healthy tissue and facilitate the simplified use of topical products.
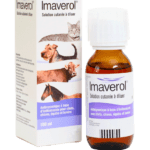
The animal must be treated with a composition that kills fungi and spores. The best for this purpose are drugs "Imaverol" and "Lime Sulfur", but you can also use shampoos containing miconazole, for example, "Nizoral". Antimycotic detergents work with direct contact, that is, they act on the pathogen during washing, but they are suitable for large animals. For example, you can wash an adult goat with shampoo, and then, if necessary, supplement the procedure with treatment. One bathing with a similar preparation is enough for a kid.
If bathing was not enough or there are deep, extensive damaged areas on the goat's body, complex treatment is used. Externally, the wounds are treated with antimycotic ointments, and inside they are given drugs for fungi such as "Griseofulvin", "Ketoconazole" or "Itraconazole". The last remedy is distinguished by the least toxicity and side effects.
The choice of drug, dosage and period of treatment are related to the type of disease, age and weight of the animal, therefore, they belong to the prerogative of the veterinarian.
Potential danger
Lichens may not appear externally or be subtle until a certain time. However, the disease develops, gradually undermining the strength of the body, weakening the immune system. In this condition, the goat can easily "pick up" any disease. Immunity may not be able to cope with colds or other diseases, so the animal will suffer or even die.
Mycoses and lichens in particular can cause a secondary infection, which further worsens the condition of the animal. From a purely technical point of view, the coat suffers, which can cause financial losses for the farmer when breeding fine-wool or downy goats. Also, lichens can cause changes in lactation, so the goat will not be able to feed the offspring or will not give enough milk if it belongs to the profile breed.
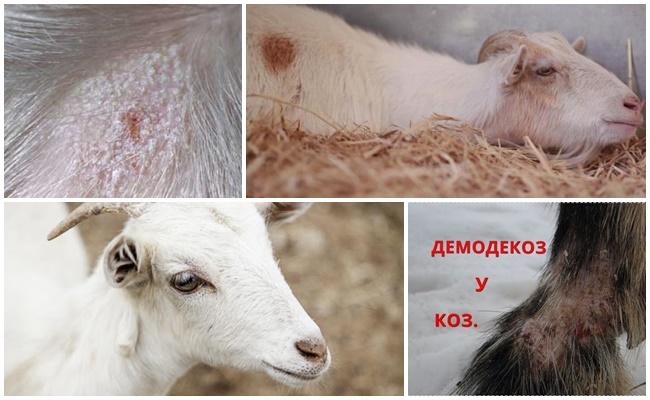
A drug for lichen can also pose a danger, in particular if the dosage or treatment time is violated. A number of drugs provoke side effects that negatively affect the functioning of the liver, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, as well as depress the function of the bone marrow.
Prevention methods
In order to avoid an outbreak of disease among goats and transmission to other animals, as well as people caring for them, it is necessary to follow these recommendations:
- Compliance with cleanliness in rooms where goats are kept.
- Cleaning, combing and, if necessary, washing animals, as fungi often develop on dirty, unkempt and matted wool.
- Isolation of an infected goat or kid to prevent the spread of lichen.
- The use of specialized vaccines.
- Balanced feeding and adherence to the rules of keeping goats contributes to a strong natural immunity, which helps not to get infected or quickly cope with the infection by the forces of the body itself.
If you provide the goats with living conditions, feed them with natural, balanced feed, and quickly begin procedures when lichen is detected, it will be possible to avoid serious losses and save the livestock, including kids and adult animals.