Instructions for the use of Epimek for goats and its composition, storage and analogues
To combat all kinds of parasites and pests, specialists have created a lot of tools. All drugs have a different principle of action, so each owner chooses the method of treatment at his own discretion. Due to its relative safety, Eprimek is popular among livestock breeders, and instructions for its use for treating goats will help effectively help pets.
Composition and release form of the drug "Eprimek"
Thanks to the active substance called eprinomectin, the agent has an antiparasitic effect. The active ingredient disrupts the work of nerve and muscle cells in the parasite's body. This leads to paralysis and death of the pest.
Benzyl alcohol, dimethylacetamide and triglyceride act as auxiliary ingredients. The drug "Eprimek" is made in the form of a clear yellowish solution for injection. Glass vials with medicine are packed in a cardboard box.
The tool belongs to a wide range of drugs. The active substances act on parasites in the larval and adult stages of development. The drug is especially effective for the destruction of nematodes parasitizing in the lungs and gastrointestinal tract of a sick animal.
The agent is easily excreted in urine and feces. Despite the fact that Eprimek belongs to low-hazard substances of group 4 (GOST 12.1.007-76), the drug should be used with caution. The product can kill bees and fish.

Indications for use
The solution is used to rid pets of various types of parasites. The drug effectively fights unpleasant diseases:
- Dictyocaulosis. The disease is caused by nematodes of the Dictyocaulus species. Pests parasitize in the bronchi of horned beauties. Involuntary "cohabitation" leads to diseases of animals with bronchitis and pneumonia. Dictyocaulosis is a common problem. Trouble often overtakes the younger generation of pets.
- Trichostrongyloidosis. The culprits of the problem are nematodes called Trichostrongylus and Haemonchus contortus. Parasites cause inflammation in the area of the digestive organs. Malaise threatens pets with weight loss, and in a neglected case, even the death of animals.
- Strongyloidosis. Helminths with the sonorous name Strongyloides papillosus cause skin inflammation, intestinal upset and even bronchopneumonia in goats. Young goats are often lagging behind in growth and development.
- Ascariasis.The disease occurs due to the nematodes Parascaris equorum. Pests affect the small intestine of the animal. The goat suffers from constant coughing, nausea, profuse salivation. Itchy rashes appear on the skin of the pet, the animal loses its appetite. With a large accumulation of parasites in the body, the animal runs the risk of dying due to severe complications in the form of intestinal obstruction, liver abscess or acute pancreatitis.
- Bunostomoz. The disease is caused by nematodes called Bunostomum trigonocephalum and Bunostomum phlebotomum. Infected goats are rapidly losing weight, and young individuals lag significantly behind their peers in development. With an advanced disease, the pet suffers from prolonged diarrhea. The animal shows signs of anemia and edema. If measures are not taken in time, the goat risks dying.
- Telyaziosis. The disease is caused by small nematodes of the genus Thelazia of the Rhodes species. They parasitize on the mucous membrane of the animal's eye. Pests infect the cornea and lead to clouding of the organ. As a result of infection, the pet is overtaken by conjunctivitis and damage to the lens.
"Eprimek" is successfully used to kill the larvae of insect pests and ticks. The drug also effectively copes with diseases:
- Hypodermatosis. The causative agent is the larva of the subcutaneous gadfly. The larvae enter the animal's body through the skin, and then through the vessels they penetrate into the spinal canal. There, pests bore fistula holes and go outside. As a result, the milk yield of animals decreases, and young individuals gain poor weight.
- Psoroptosis. The disease is known as scabies on the skin. Mites of the genus Psoroptes cause trouble. They cause unbearable itching of the skin. In the affected areas, the skin is inflamed, the animal's hair falls out. Yellow crusts form on the affected areas of the body.
- Syphunculatosis. The causative agents of an unpleasant disease are lice. Pests successfully parasitize all types of mammals. Lice feed on animal blood, causing unbearable itching in victims. The pet is combing the affected areas, injuring the affected skin. As a result, the pet develops dermatitis, hair falls out. Adult animals lose appetite and lose weight, and young goats are lagging behind in development.
The drug is also used to combat carrion flies. Disgusting insects gladly settle in the wounds of animals and often cause parasitic diseases.
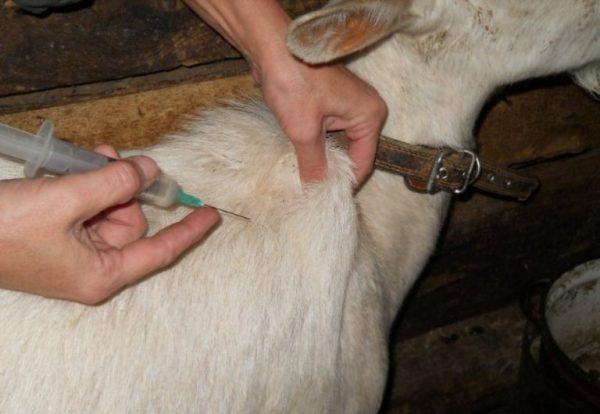
Instructions for using veterinary medicine for goats
According to the instructions for use of the veterinary drug for goats, the solution is administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly. The dosage of the drug is taken on the basis of the calculation: 200 μg of the active substance for each kg of the pet's weight or 1 ml of the solution for 50 kg of the animal's weight.
To get rid of the nematodes, the goat is injected 2 times. The first one is in the spring, before the pet leaves the pasture. The second procedure is done at the end of summer, before sending the pets to the "winter apartments". To combat gadfly larvae, the injection is done at the end of the summer season.
Repeat the procedure if necessary. The interval between injections should be at least 14 days. Mixing of the drug with other substances in one syringe is not allowed. Slaughter of animals intended for meat is performed only after 28 days after the last injection. Otherwise, the meat of sick goats is used only as feed for fur animals, as well as for the production of fertilizer (meat and bone meal). The milk received from the pet can be eaten safely during the treatment period.

When working with a solution, you must adhere to the general rules. After using the drug, wash your hands thoroughly with soap. If the product gets on the delicate mucous membrane of the eyes, rinse them with water.Do not use empty medicine containers for household needs.
Side effects
Exceeding the dose of the drug causes a deterioration in the condition of the pet. Side effects of the goat include prolonged diarrhea and uncontrolled salivation. The animal becomes agitated.
In case of individual intolerance to individual components of the drug, a goat has an intestinal disorder, frequent urge to urinate and impaired coordination of movements.
In both cases, medical attention is not required, the side effects will gradually disappear, and the goat's health will return to normal. In the case of a pronounced allergic attack, the pet is given an antihistamine.

Contraindications
The drug should not be given to individuals suffering from intolerance to avermectins (waste products of Streptomyces avermitilis fungi). Also, the remedy should not be prescribed to young goats (up to 4 months).
How and how much can you store
Eprimek can be stored in a dark, dry place. The optimum storage temperature is from 5 to 25 degrees. Opened vials keep up to 28 days. After the expiration date, the remaining solution is disposed of.
Similar means
The drug "Eprimek" is successfully replacing similar drugs: "Alezan" (Russia), "Equisect" (Russia), "Panakur" (France), "Ivermek" (Russia).









